
 Posts
Posts Likes Received
Likes ReceivedWalking through the "bitterness and happiness" of the epidemic, where is Uber's future path? input: ====== 2021 年 2 月,我们发布了一份报告,分析了长桥海豚的 2021 年第一季度及全年的发展前景,认为当前海豚季度和全年表现评级为 “跑赢大市”,对应目标价 212 港元,相对当前股价上升逾 30%。 在过去的三个月中,长桥海豚跑赢大市。 ====== output: In February 2021, we released a report analyzing Dolphin's development prospects for the first quarter and full year of 2021. We believe that the current performance rating of Dolphin for the quarter and full year is "outperform," with a corresponding target price of HKD 212, which is up more than 30% relative to the current stock price. Over the past three months, Dolphin has outperformed the market.

Combining with Dolphin Analyst's analysis on Uber's deep analysis and the recent study on the future trends of the US economy, we believe that the fundamental reason why Uber can safely overcome the impact of the epidemic in 2020-21 and stand out in the post-epidemic era after 2022 is that Uber is one of the very few internet platforms that have both ride-hailing and food delivery businesses and have achieved industry-leading scale.
With this advantage, the surge in food delivery demand during the epidemic offset the significant decline in ride-hailing business. Meanwhile, the rapid recovery of offline ride-hailing demand in the post-epidemic era also compensated for the stagnation of food delivery business growth. From a short-term perspective, the company has achieved good performance in the second and third quarters of this year under the bonus of the recovery of offline activities.
However, although most of the current economic indicators in the United States are performing well and there is no obvious sign of recession, the high inflation eroded the significant savings accumulated during the epidemic by US residents in the past year. The ratio of monthly new disposable income to per capita consumption has also plummeted to only 1.07, the lowest level since 2000.
In summary, US residents currently have no savings and monthly new income can only cover their monthly expenses by a ratio of 1.07:1. Looking ahead to the fourth quarter and 2023, there is a significant chance that personal consumption expenditures, which account for more than 70% of US GDP, will begin to decline, thereby dragging down the entire macroeconomic downturn.
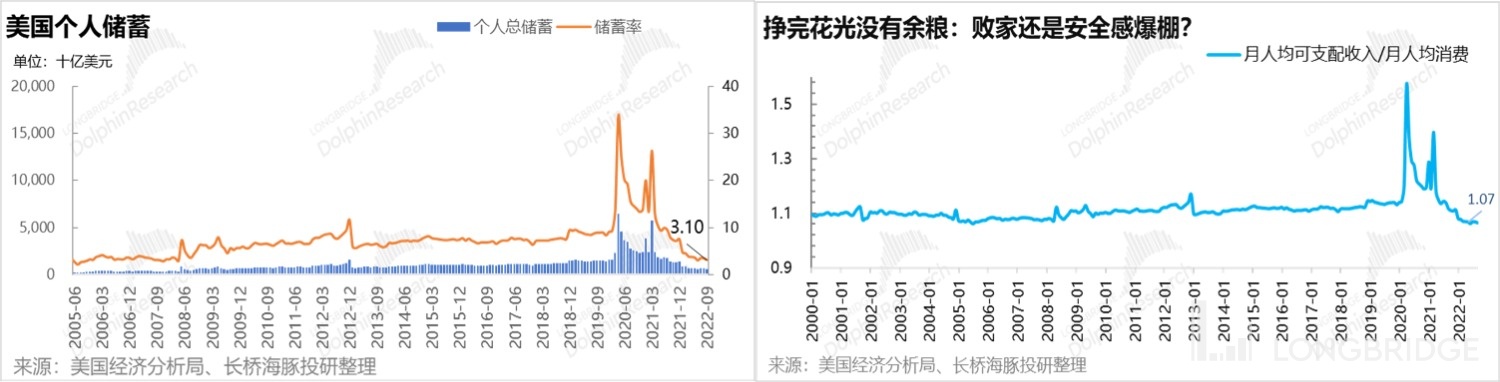
Dolphin Analyst believes that as US residents' consumption may gradually decrease in the next few quarters, there is a good chance that Uber's performance will also weaken or even slightly shrink until the second half of 2023, after which it will return to steady growth. Therefore, after the market's rebound and valuation repair of Uber's sentiment bottomed out since the business performance exceeded expectations in the second quarter, the logic of investment and the market's focus will return to the long-term profit space and long-term growth of ride-hailing and food delivery businesses after the epidemic has no impact. Therefore, this article will try to calculate the reasonable valuation of Uber based on its long-term growth potential and steady-state profit margin.
To conclude, firstly, Dolphin Analyst believes that ride-hailing business still has long-term growth potential, given a low user penetration rate despite ten years of development. Moreover, by constantly expanding the types of ride-hailing products, such as U4B for business-to-business, Uber Reserve which allows advance bookings, and the ride-sharing service UberX Share, providing more choices can also increase user frequency. Therefore, we estimate that the compound annual growth rate of Uber's ride-hailing revenue can reach 10.4% from 2022 to 2027. 2) For the delivery business, the Dolphin Analyst believes that the working hours and consumption habits of European and American residents make the long-term growth space of food delivery not as huge as in China. The forecasted compound growth rate of food delivery orders is only 5.7%. However, outside of food delivery, the penetration rate of non-food categories (daily necessities, supplies) is still low, and the market size is huge. The expansion of delivery categories can bring additional growth. In fact, Uber has also acquired grocery delivery company Postmate and liquor delivery company Drizly. According to Dolphin's prediction, after adding non-food delivery, Uber's overall revenue compound growth rate can still reach 11.5%.
3) In terms of gross profit margin, since the company's realization rate naturally tends to increase as the average unit price and unit efficiency increase, while costs mostly increase with the growth of order volume or order amount. Therefore, most of the improvement in the realization rate can be transformed into profit improvement. Based on Dolphin Analyst's detailed breakdown of the realization rate and cost predictions, Uber's overall gross profit margin is expected to increase from 38.3 in 2022 to 47.4% in 2027.
4) Therefore, based on the above predictions, assuming a risk-free rate of 4% and WACC = 10.4%, Uber's current fair value is $39, which is 35% higher than the current market price of $29.
However, from another perspective, the reason why the market is currently unwilling to give Uber a higher valuation should be: 1) The prospects for non-food delivery, the main driving force of incremental growth, are not clear; 2) Neither ride-hailing platforms (Uber, DiDi, Lyft) nor food delivery platforms (Meituan, DoorDash, Uber Eats) have been able to generate stable profits, so the market has no confidence and reference standards for the long-term stable profit of Uber; 3) Uber's profits are all in the future, and a slight increase in the discount parameter can cause a significant decrease in the company's valuation. The WACC that the market actually requires for Uber may be higher than what the Dolphin Analyst expects.
Dolphin Investment Research focuses on interpreting global core assets across markets for users, grasping the deep value of enterprises and investment opportunities. Interested users can add the WeChat account "dolphinR123" to join the Dolphin Investment Research community and discuss global asset investment viewpoints together!
I. After getting through the epidemic, stable growth rate is the core issue
For a platform-type company, predicting the total amount of orders on the platform is the basis for analyzing revenue, profits, and future prospects. In terms of the analytical framework, because the order amount (Gross Booking) = active users \ frequency of an individual user placing an order \ average order price**, it can be seen that the steady growth potential of different business order amounts of Uber depends on the different combinations of the above three variables. Therefore, this chapter will focus on these three variables.
First of all, regarding the company's online car-hailing business, the trend has been rapidly rebounding since the omicron outbreak. By the third quarter of this year, the order amount scale has exceeded about 10% of the same period in 2019. However, considering the price-volume perspective, since the price of gasoline has more than doubled before the epidemic, the average unit price of online car-hailing, according to the survey, has increased by more than 50% compared to 2020. Therefore, it can be inferred that Uber's online car-hailing order volume has not actually recovered to the level prior to the epidemic.
After combining with the overseas investment bank's forecast, the Dolphin Analyst separately split the monthly active users and order data of the online car-hailing business (the company only disclosed the overall data for hailing taxis and takeaways). It was found that even after the rapid rebound in the first half of 2022, the monthly active users of the hailing taxis have currently returned to about 95% of the level in 2019. The average number of orders per monthly active user has also recovered to about 90% at the end of 2019. Although the control measures for the epidemic in Europe and the United States have basically ended, the frequency of users traveling offline and using online car-hailing is still yet to return to the pre-epidemic norm. From another perspective, with the complete fading of the epidemic, there is still hope for the monthly activity and order frequency of online car-hailing to continue to recover.
However, as for the short-term trend of the online car-hailing business, the biggest focus and question for the market is, as a "mature" business that has been developing for more than ten years, what is the potential for long-term growth after fully recovering to the pre-epidemic level? To answer this question, let's start by looking at the user base of Uber's online car-hailing service. Uber's business currently covers dozens of countries worldwide, and the user penetration rates in different regions vary. According to the company's disclosure, as of the end of 4Q19, Uber's online car-hailing users had the highest penetration rates in Brazil and Australia, reaching 6%~7% of the local population. While in the largest market - the US, Canada, and the UK, the user penetration rate still has 75% room for improvement compared to Australia, and the user penetration rate in other newer markets is only around 1%. Overall, according to statistics from Morgan Stanley, in 2021, the total number of online car-hailing users of Uber accounted for only 3.1% of the total population of 2.5 billion in all regions covered, which means that a 1% increase in user penetration rate could bring in 25 million new users.
Although we cannot simply assume that the user penetration rate in all countries can eventually reach the level of Brazil or Australia, at least we can draw the following conclusion: although online car-hailing has developed for more than 10 years, the user penetration rate is still only in the low single digits. Unlike e-commerce or social internet services, it still has great potential for improvement in the penetration rate, indicating that online car-hailing is still in its "youth" stage. From the perspective of the frequency of orders from individual users, although the overall demand for online car-hailing was suppressed during the epidemic, the actual effect of the epidemic on long-term awareness of user travel channel choices is favorable to online car-hailing. Based on New York City's travel data, during the epidemic, the proportion of online car-hailing to public transportation increased from 10% before the epidemic to 15%, and even though it has recently fallen, it still remains at around 12.5%. Therefore, the epidemic has made users prefer to use relatively private and safe online car-hailing, and this trend will continue even in the post-epidemic era.
In addition to industry trends, Uber itself continues to expand its online car-hailing product types, which will also promote an increase in user order frequency. In addition to the two car models Uber Black and SUV that Uber launched when it was founded, the company has now greatly expanded its product line. According to the company's statistics, the order frequency and retention rate of users who use multiple product types are significantly higher than those who only use a single product.
From the perspective of per customer spending, online car-hailing per customer spending has also increased significantly in the past two years due to the continuous rise in labor and gasoline prices. However, looking to the future, with the trend of weak global economic growth, the market generally believes that demand for oil and its prices will decline. According to Bloomberg's statistics, it is expected that crude oil prices will decrease by 3%, 10%, and 3% respectively between 2023-2025. Therefore, considering that oil prices are expected to decline and that demand for online car-hailing may decline due to macroeconomic impacts in the next few quarters, Dolphin Analyst believes that online car-hailing per customer spending will decline year-on-year in 2023-2024. However, considering another pricing factor of online car-hailing, driver labor costs have historically only risen and never fallen, so the magnitude of the decline in per customer spending should be less than the fluctuation of oil prices.
Overall, looking at the trends in the three main factors of monthly active users, order frequency, and per customer spending, Dolphin Analyst believes that user growth will be the main driving force for the online car-hailing business. Per customer spending will decrease and then increase again due to fluctuations in gasoline prices over the period 2023-204. Meanwhile, the increase in order frequency will also have space for long-term growth, but it will be relatively slow and may decrease and then increase again around 2023 due to a decline in consumer spending by residents.
Taking into account the impact of these three key factors, Dolphin Analyst predicts that the online car-hailing order amount will increase from approximately 51 billion yuan in 2022 to approximately 79.6 billion yuan in 2027, with a CAGR of approximately 9% over the next five years.
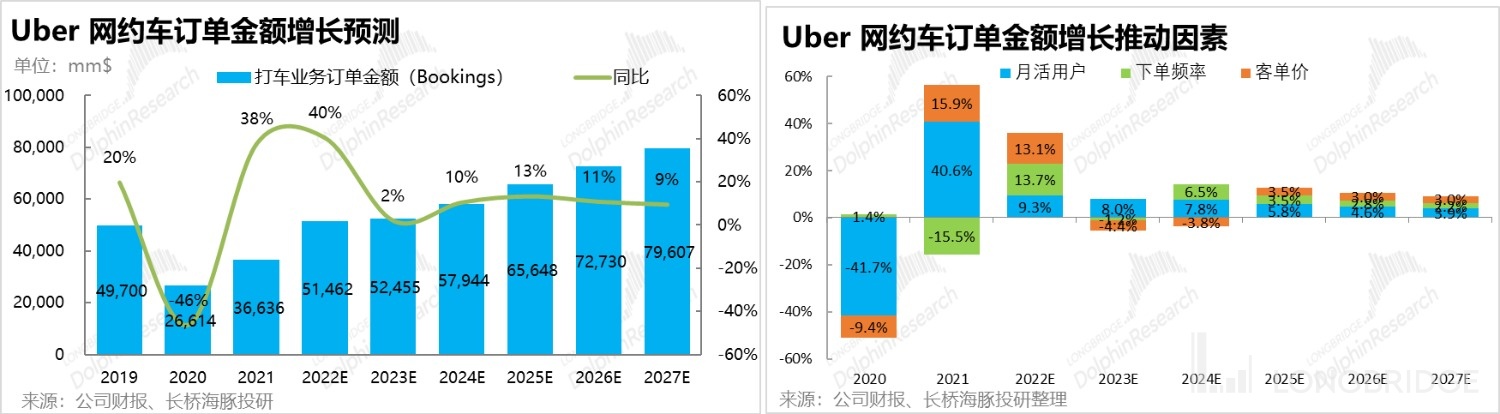
Based on the above predicted total turnover of Uber ride-hailing orders, the next step is to analyze the process of converting order amount into revenue for the company. Generally speaking, there are three items of order amount that need to be paid out, including taxes & tolls, driver income, and incentives given by Uber to the driver. The remaining part is Uber's realization part, that is, revenue. Specifically:
-
First of all, operating taxes and tolls, which are relatively fixed costs, currently account for about 7% of the total order amount, and we expect it will remain stable at that level in the future.
-
The second largest segment is the income of ride-hailing drivers, including regular income and driver incentive income. It can be seen that before this year, the proportion of driver income to order amount has remained stable at around 69%. In 2022, it decreased significantly to 64%, but this was not due to a decrease in driver revenue sharing, but because Uber in the UK switched its business to self-operated mode, and the driver revenue sharing is no longer considered a deduction from revenue, but reflected in operating costs (cost of sales).
Looking ahead, the Dolphin Analyst believes that income level is the primary reason for drivers to choose a platform, and the inherent weak bilateral effect and low cost of driver switching for ride-hailing platforms mean that Uber must continue to provide attractive driver revenue sharing.
Therefore, we believe that the overall normal income of Uber drivers per order will follow the changes in unit price, but it is relatively easier to increase than decrease. As for the additional incentives given by Uber to drivers, they will likely quickly decrease from the exceptionally high values during the pandemic period. Overall, the average total revenue per order for Uber ride-hailing drivers will also decrease slightly in 2023-24, and then stabilize and increase at a rate of 2.5%.
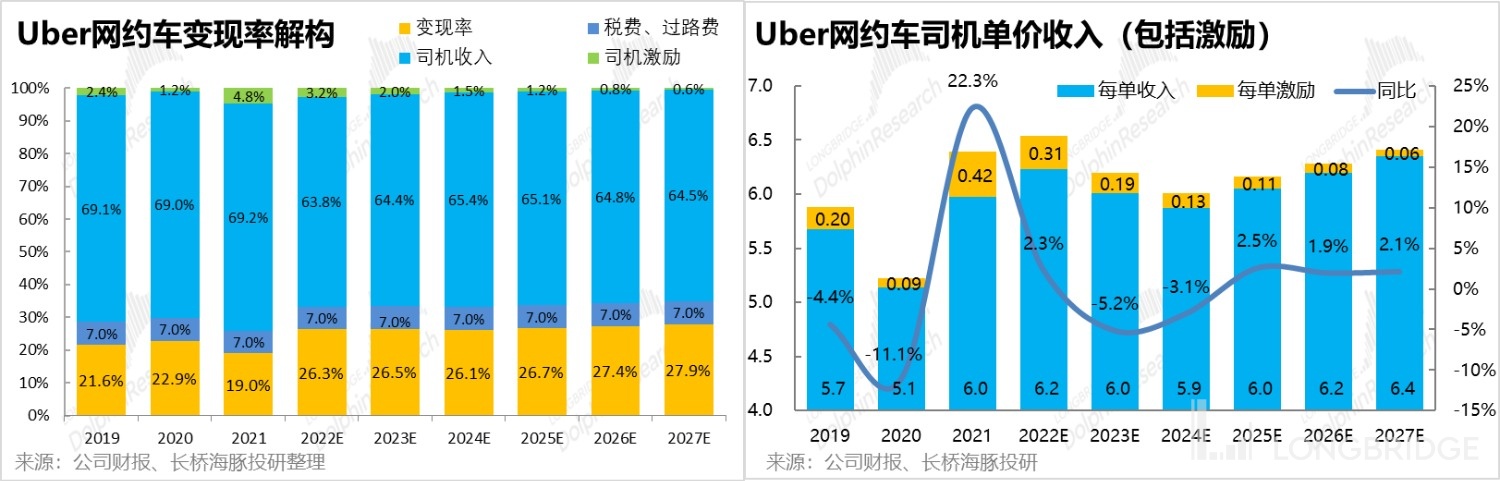
Overall, we conservatively predict that the normal per-order revenue sharing for drivers will steadily increase, but with the reduction of incentives, the actual monetization rate of Uber ride-hailing still has room for improvement, from a slight increase of 26.3% in 2022 to 27.9% in 2027. Therefore, the revenue of the Uber ride-hailing sector can still grow at a compound annual growth rate of 10.4% from 2022 to 2027.
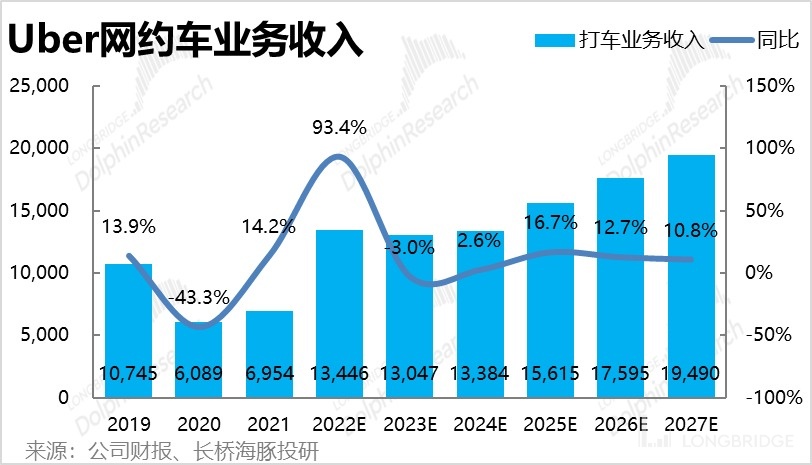
2. Takeaway business: Extra growth depends on category expansion
For the takeaway business, it can be seen that since the second quarter of 2022, the order amount has continuously declined for two consecutive quarters, and the year-on-year growth has also dropped sharply to only a single digit. The Dolphin Analyst believes that the relatively lenient working hours and wider offline dining habits of European and American consumers mean that the long-term ceiling and growth potential of catering takeout are not as high as those in China. However, in the short to medium term, due to the recovery of offline activities and the overall decline in consumer spending by Europeans and Americans, it is very likely that the demand for dining takeaway by consumers may temporarily decrease, according to Dolphin Analyst.
According to predictions from third-party organizations, the annual increase in the penetration rate of platform-based takeaway users in the United States will drastically decrease to 0.4-0.5% since 2023. Compared with the average penetration rate increase of only 1% between 2021-2022, excluding the exponential surge from 2019 to 2020, it is obvious that the growth of takeaway business users in the market is expected to slow down significantly.
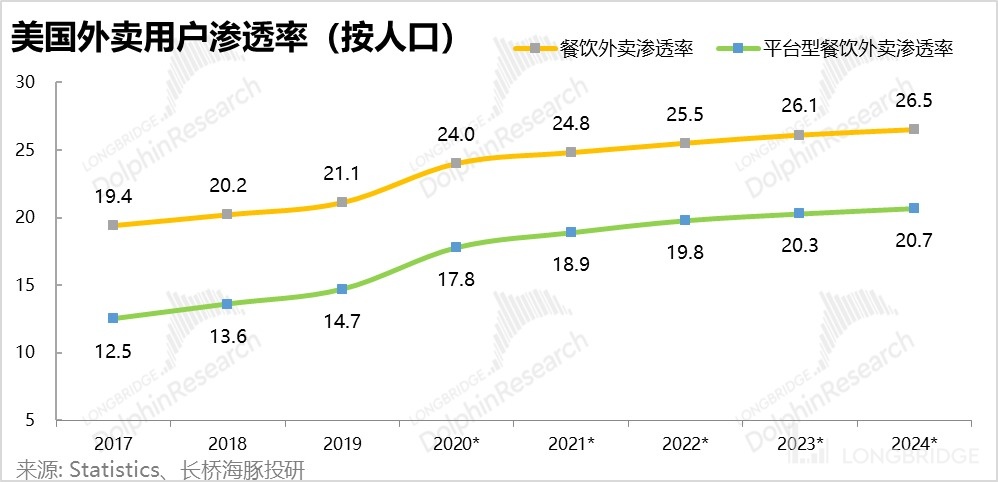
According to our predictions, Dolphin Analyst expects that in 2023, there will be a year-on-year deterioration in the number of users and ordering frequency for takeaway services due to the recovery of offline activities and the decline in consumption, and the prospects for growth in the long term are not great. As for the actual takeaway service per order price, except for a year-on-year growth reaching double digits in 2020-21, it has only increased by a low single-digit number every year from 2017-19 and in 2022, so we predict that the growth rate of per order price will return to the low single-digit number norm, even after 2023.
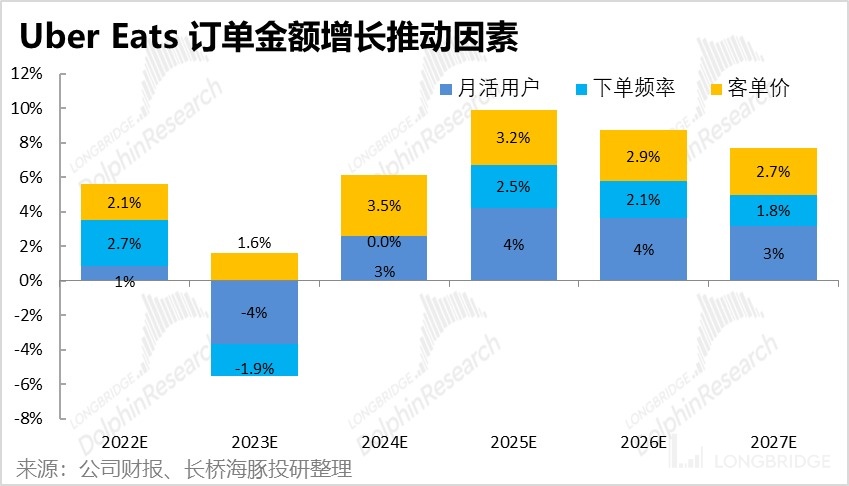
Based on the expectations for the three factors of the number of users, ordering frequency, and per order price, we predict that the composite annual growth rate of the amount of takeaway orders in the food and beverage industry will drastically decrease to 5.7% from 2022-2027.
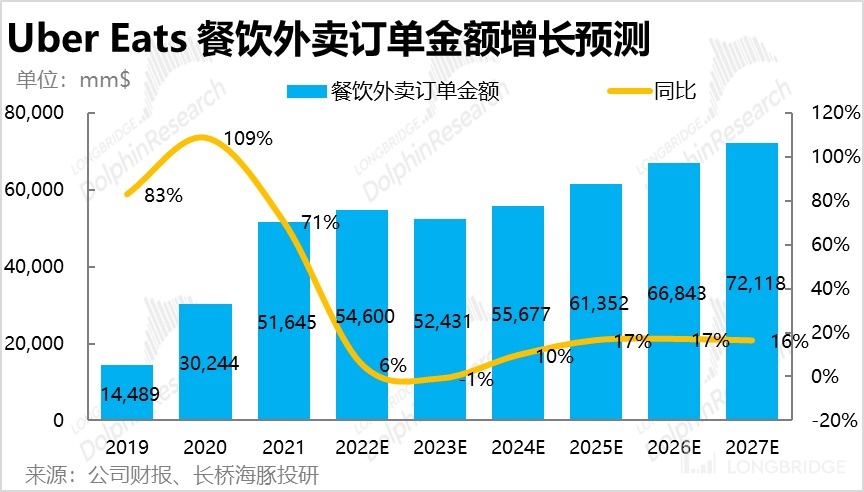
However, although the growth of takeaway services will slow down after the epidemic bonus period, expanding to other daily necessities, alcoholic beverages, and other areas can bring additional growth space to Uber Eats. Uber's acquisition of comprehensive takeaway company Postmate and alcohol delivery company Drizly both reflect the company's strategic direction of expanding takeaway categories and the potential market size (TAM). In comparison, domestically, Meituan also takes the same growth logic of penetrating from high frequency dining to other daily necessities categories.
Moreover, according to institutional statistics, the online penetration rate of food daily necessities and alcoholic beverages is only around 12% and 1.6% in 2022, respectively. Compared with the current online retail penetration rate of around 20% in the United States, the penetration rate of the two major categories is obviously low, so the space for online growth in these two categories will also be greater.
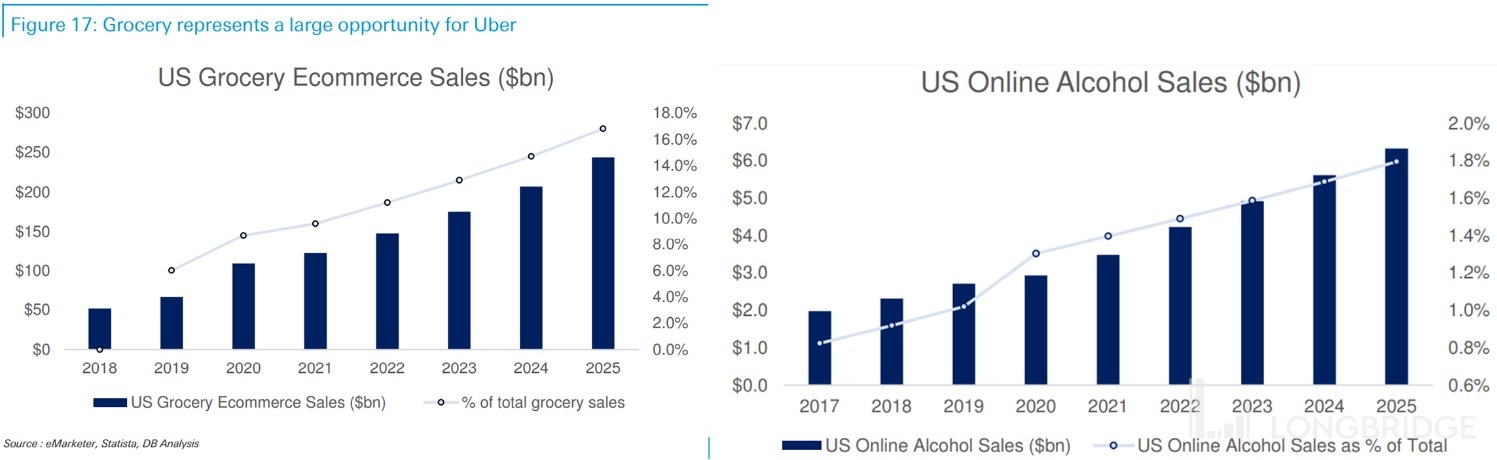 According to the market size growth rate statistics referenced by Statista, it can be clearly seen that the scale growth rate of daily grocery take-out category in the future is significantly higher than that of catering take-out.
According to the market size growth rate statistics referenced by Statista, it can be clearly seen that the scale growth rate of daily grocery take-out category in the future is significantly higher than that of catering take-out.
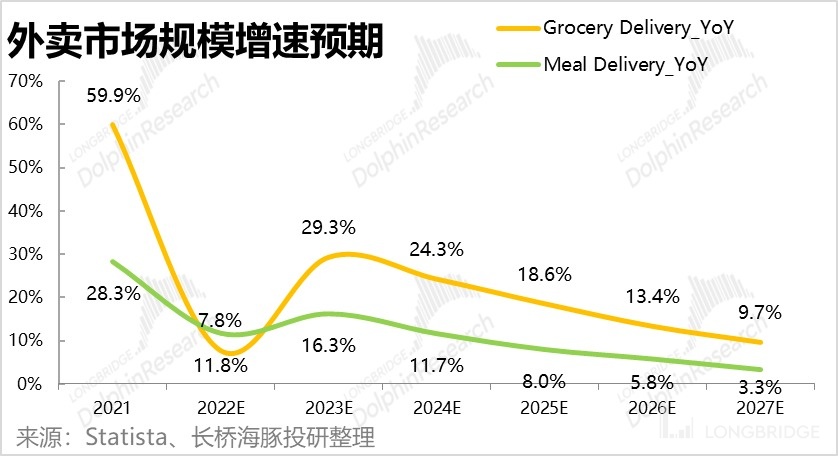
From the above, it can be seen that non-catering takeout is an extremely potential second growth point. Therefore, Dolphin Analyst predicts that: 1) the monthly active users of non-catering takeout will reach 70% of catering takeout users; 2) the ordering frequency of non-catering takeout will reach once a month; 3) in terms of the customer unit price, by referencing the customer unit price of instant delivery platforms for daily necessities in China and calculating according to Dolphin Analyst, the per capita purchase amount of Walmart, the European and American supermarket leader, is around 40-50 US dollars. It is predicted that the customer unit price of Uber non-catering takeout will reach 45 US dollars.
Based on the above assumptions, it is estimated that the order amount of non-catering takeout will exceed 22 billion US dollars by 2027, which is equivalent to about one third of the order amount of catering takeout. With the incremental contribution of non-catering takeout, the compound growth rate of the overall order amount of the takeout business can be increased to 11.5% from 2022 to 2027.
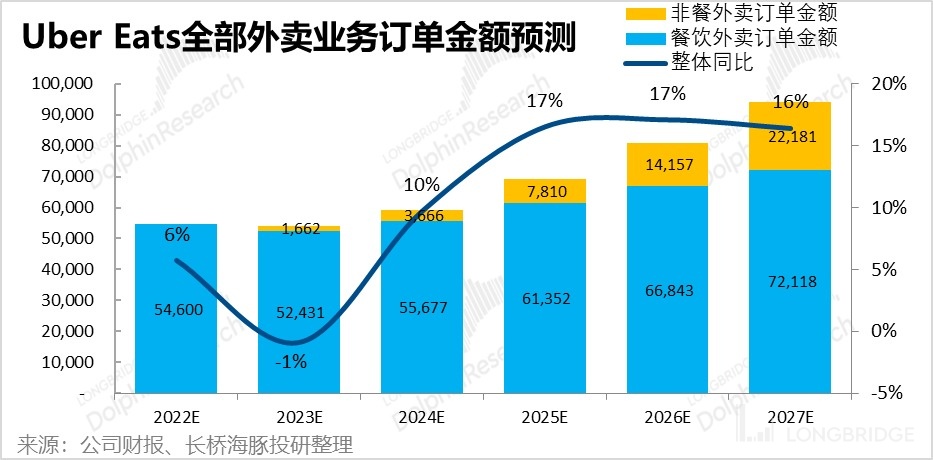
Looking at the structure of the order amount of the takeout business, it mainly consists of three parts: 1) tax and fee, which takes a relatively fixed proportion of the total amount;
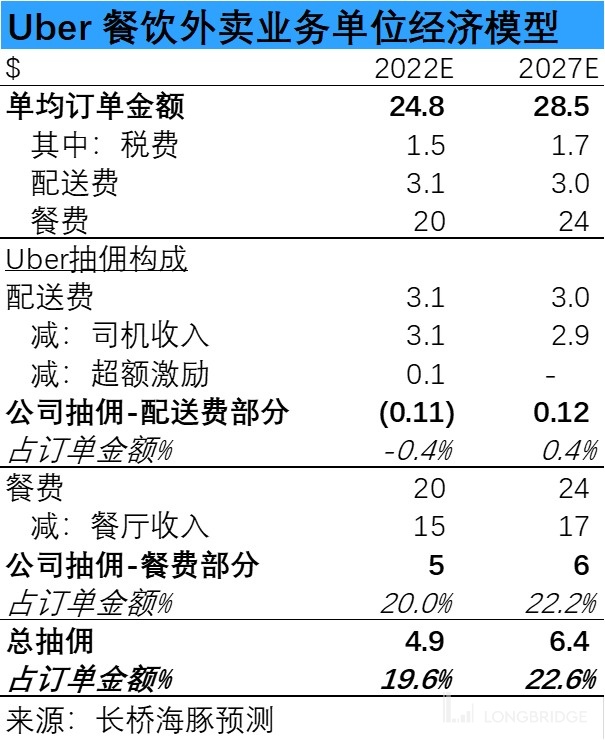
- the delivery fee part, which accounts for about 12.5% of the order amount in 2022. In the long term, Dolphin Analyst believes that the growth of order volume will drive a decrease in the average delivery fee, but the inflation of delivery staff's labor costs will limit the downward space of the delivery fee.
However, at present, Uber basically transfers all the delivery fee revenue to the delivery staff, and even provides additional incentive income, resulting in a negative realization rate of the company's delivery fee.
But by 2027, Dolphin Analyst assumes that Uber will take 5% of the delivery fee as the company's revenue and completely cancel the additional incentives. Then, the commission extracted by the company from the delivery fee will be 0.12 US dollars, accounting for 0.4% of the order amount.
- the meal fee part, that is, the remaining part of the order amount excluding tax and fee and delivery fee. Combining with the predictions of foreign banks, Dolphin Analyst conservatively predicts that the proportion of commission extracted from meal fee will slightly increase to 26.5% in 2027. In this case, in 2027, Uber will extract 6.3 US dollars from each order in terms of meal fee, accounting for 22.2% of the total order amount. And the total commission rate of company meal fee + takeout fee can increase from 19.6% in 2022 to 22.6%.
 For non-food delivery services, Dolphin Analyst did not provide a detailed breakdown of their predictions. However, considering that the gross profit margin in supermarkets is generally below 30%, while the gross profit margin in catering can reach 50-60%, the commission rate that Uber can extract from non-food delivery services will be significantly smaller. Dolphin Analyst assumes that the monetization rate can reach 12.5% by 2027.
For non-food delivery services, Dolphin Analyst did not provide a detailed breakdown of their predictions. However, considering that the gross profit margin in supermarkets is generally below 30%, while the gross profit margin in catering can reach 50-60%, the commission rate that Uber can extract from non-food delivery services will be significantly smaller. Dolphin Analyst assumes that the monetization rate can reach 12.5% by 2027.
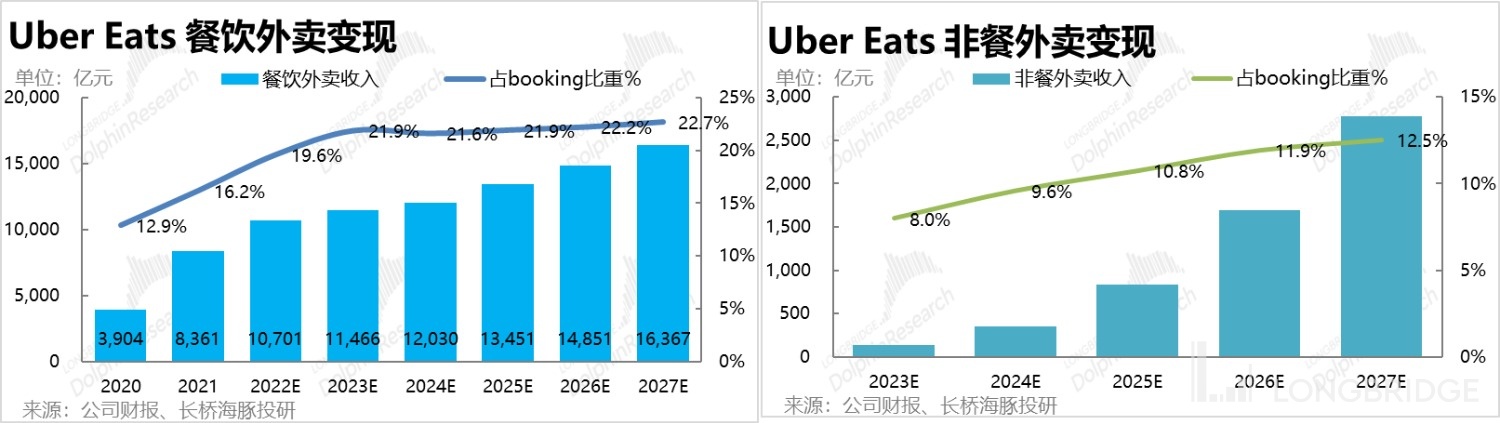
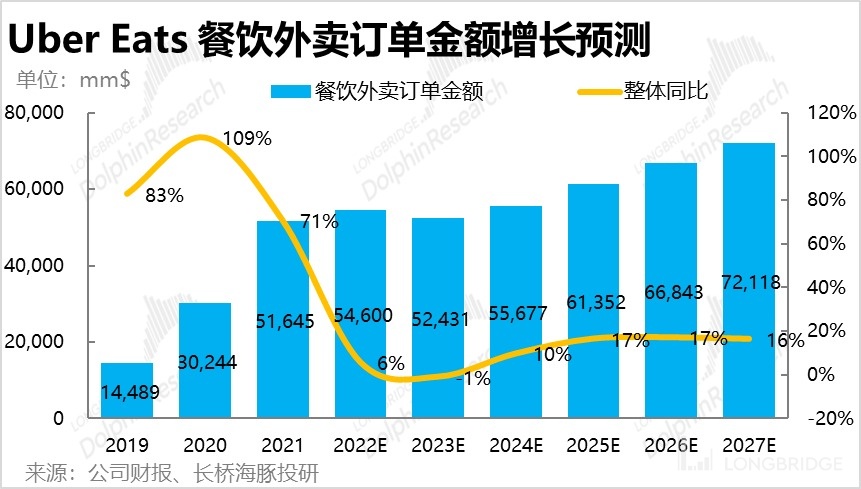
Combining the revenue forecasts for food and non-food delivery services, Dolphin Analyst estimates that the total revenue for delivery services can grow from RMB 54.6 billion in 2022 to RMB 72.1 billion in 2027, a compound annual growth rate of 12.3%.
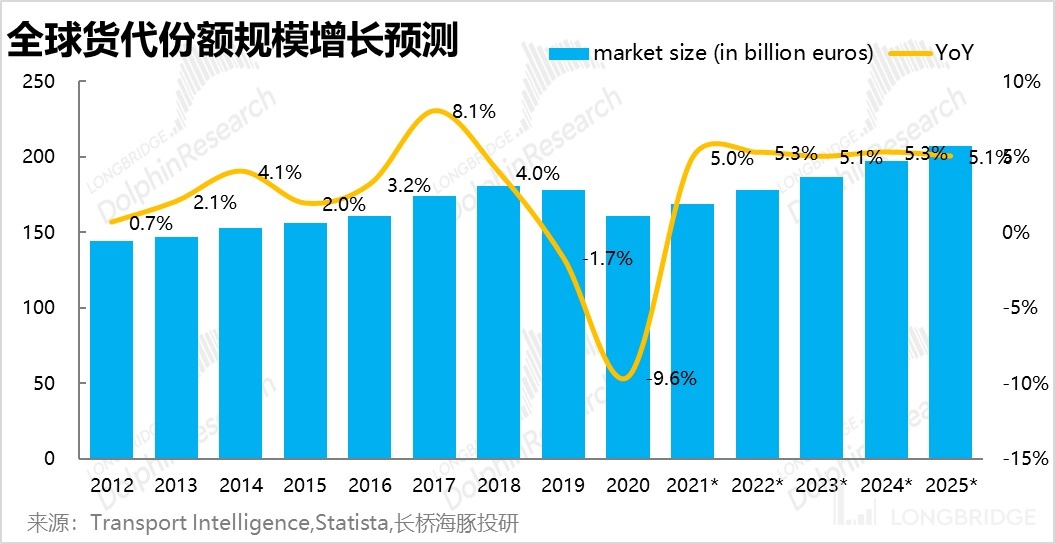
- The freight forwarding industry under "sunset" may not bring much growth.
For Uber's non-core freight forwarding business, due to its small revenue share and almost zero adjusted EBITDA contribution, the market generally does not pay much attention to this segment. Moreover, as a very mature traditional industry, the annual growth rate of freight forwarding transportation fluctuated mainly in the range of 2%-4% before the epidemic, and the industry has basically had no increment, just following price inflation. Looking ahead to 2022, professional third-party organizations predict that the compound annual growth rate of freight forwarding business will remain at 5%. Dolphin Analyst believes that the above prediction is actually slightly optimistic, as the growth rate of freight forwarding business during the epidemic when international freight transport was extremely scarce was only 5%.
In fact, judging from the revenue growth rate of Uber Freight itself, after deducting the contribution of Transplace, we estimate that the revenue growth rate of Uber Freight's original business has fallen to around 10% in 2022, after experiencing high growth during the epidemic, and has passed the stage of rapid expansion of new business.
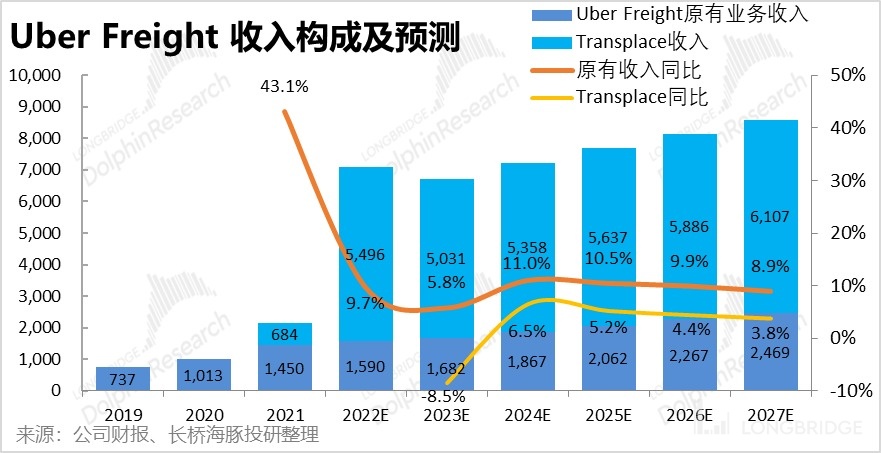
Looking ahead to the future, we predict that Transplace's revenue will decline in 2023 due to its high base and the global economy entering a downturn, and will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.6% following the market trend in 2024-27. For Uber's original freight business, due to its unique 2B platform business model and the logic of penetration rate improvement, we predict that it can grow at a CAGR of about 9.2%, which is twice the industry average growth rate. After adding the two sections, Uber Freight's total revenue will increase from USD 7.08 billion to USD 8.6 billion between 2022 and 2027.
2. What is Uber's cost structure and where is the optimization space?
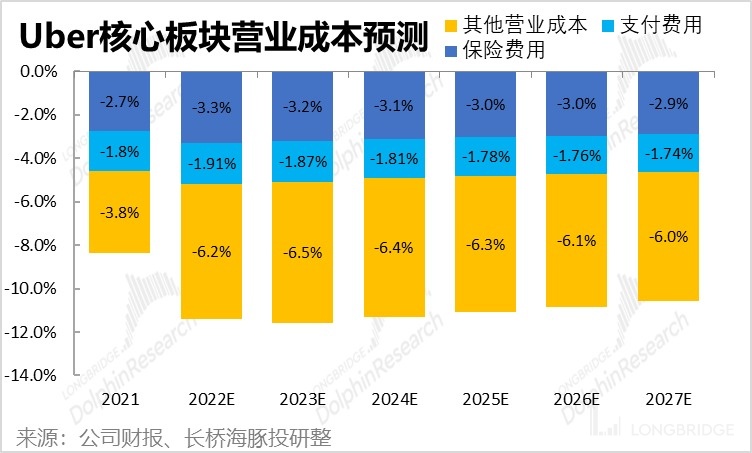
For the company's core ride-hailing and food delivery businesses, operating costs are mainly composed of three parts: 1) insurance premiums paid by the company for the ride-hailing and food delivery businesses, 2) payment fees that the company needs to bear when customers pay for ride-hailing or food delivery, and 3) other server and related costs. This also includes driver salary expenses that need to be included in costs after the company changed to a self-employment model in London.
Whether it is insurance premiums, payment fees, or server costs, they are mostly accompanied by an increase in order volume or order amount. As a result, with the improvement of the monetization rate promoting revenue growth higher than the order amount growth rate, gross profit margin has an inherent upward trend.
Specifically, we believe that as the order size increases, the average insurance premiums and payment rates will both have a slight downward trend. In addition, the insurance premium rate for ride-hailing services will be higher than that for food delivery services (food delivery only insures the riders, while ride-hailing requires both the driver and the passenger to be insured). Therefore, as the proportion of food delivery business increases, the overall insurance premium rate of the company will also decrease.
As for other costs, which include driver salaries for self-employment businesses, Dolphin Analyst believes that because the average price of ride-hailing and food delivery businesses may decrease year on year between 2023 and 2024, but driver salary costs cannot be reduced easily, it is expected that the proportion of this cost will slightly increase in 2024 and then gradually decrease.
Because Uber Freight's logistics business records 100% of the order amount as revenue, the gross profit margin cannot be as high as the ride-hailing and food delivery businesses that only have a commission as income. In addition, considering that companies in the logistics and cargo industry generally have a net profit margin of only a single digit percentage, we assume that the gross profit margin of the Uber Freight business can increase from the current less than 5% to about 15% in 2027.
Based on these assumptions of the various cost items, Dolphin Analyst estimates that Uber's overall gross profit margin is expected to increase from 38.3% in 2022 to 47.4% in 2027. The fundamental reason for the improvement in gross profit margin is still the improvement in average unit cost and the improvement in monetization rate after scaling up.
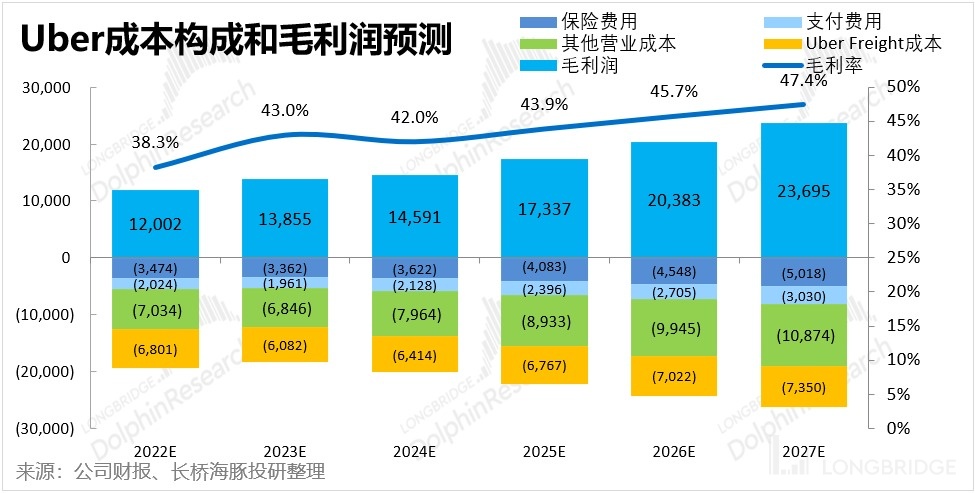
3. Profit forecast and valuation
In terms of costs, Dolphin Analyst believes that under the company's strategic direction of turning losses into profits, except for research and development expenses, the growth rate of the other three expenses will significantly slow down. However, from a cautious perspective, Dolphin Analyst does not blindly assume that cost reduction will lead to profit release. Instead, the expected ratio of operating expenses to total revenue will narrow from 44% in 2022 to 38% in 2027, with an average annual reduction of 1.2 percentage points. Therefore, according to Dolphin Analyst's prediction, the improvement of the company's profits mainly relies on the improvement of the gross profit by increasing efficiency. Eventually, Uber's overall operating profit margin is expected to reach 9% in 2027, achieving an operating profit of 4.49 billion US dollars. Dolphin Analyst believes that in platform-based internet platforms, a 9% operating profit margin is a relatively low level and should be considered a relatively conservative prediction.
Based on the aforementioned profit expectations, assuming a risk-free rate of 4% and a WACC of 10.4% to reflect the expectation of the Fed's interest rate hike, Dolphin Analyst estimated the current fair value of Uber to be $39, which is 35% higher than the current price of $29. Therefore, according to Dolphin Analyst's expectation that Uber can maintain a 10% compound revenue growth rate from 2022 to 2027 and increase the operating profit margin to 9%, Uber still has a good return potential.
However, looking at it from another perspective, Dolphin Analyst believes that the market's unwillingness to give Uber a higher valuation is mainly due to two reasons: 1) Whether the takeaway business can continue to achieve a compound growth rate of more than 10% after the epidemic mainly depends on the contribution of non-meal takeaway business, but the prospects of this part of the business are unclear; 2) Worldwide, both ride-hailing platforms (Uber, DiDi, Lyft) and food delivery platforms (DoorDash, Uber Eats) outside of Meituan have not been able to generate stable profits, so there is no reference and confidence in the market for Uber's long-term steady-state profits.
In addition, from the perspective of WACC, since the company's profits can only be released after several years, changes in the discount rate parameters also have a considerable impact on the company’s valuation. Referring to the table below, when the company's perpetual growth rate is reduced to 2% and the WACC is increased by 1 percentage point to 11.4%, the company's fair value is the current price.
Past analysis articles on Uber by Dolphin Research:
Financial Reports
November 2, 2022, Phone Conference Call "Uber believes that travel demand is still strong, and the focus in the future is to improve user stickiness and habits (3Q22 conference call minutes)"
November 2, 2022, Financial Report Review "Can Uber make a profit without growth and the market still buy it? " invite-code=EZND0I&channel=t3586604)》
Insight
On October 14th, 2022, "Through Epidemics and Inflation, the Killer Move Behind Uber's Luck" (source) was published.
Risk Disclosure and Statement for this article: Disclaimer and General Disclosure for Dolphin
The copyright of this article belongs to the original author/organization.
The views expressed herein are solely those of the author and do not reflect the stance of the platform. The content is intended for investment reference purposes only and shall not be considered as investment advice. Please contact us if you have any questions or suggestions regarding the content services provided by the platform.


