
Down 34%, what happened to Porsche in China?

Porsche's sales in the Chinese market continue to decline, with cumulative sales of only 48,000 units from January to November 2024, a year-on-year decrease of 34%. Since 2015, China has been Porsche's largest single market, but its attractiveness has weakened after 2022, with sales declining for two consecutive years. Factors such as intensified market competition, changing consumer preferences, and the impact of the macroeconomic environment may contribute to this trend. Porsche's sales in China show significant fluctuations, with sales of 6,662 units in January 2024, dropping to 2,789 units in February, rebounding to 4,139 units in March, and slightly decreasing to 4,063 units in April
Once, Chinese users were an indispensable pillar of Porsche's market. Since 2015, 14 years after entering the Chinese market, Porsche's sales in China surpassed those in the United States for the first time, making China the brand's largest single sales market globally, a position it has maintained for six consecutive years.
However, by 2022, Porsche's appeal in China began to wane, leading to a decline in sales in the Chinese market for two consecutive years.
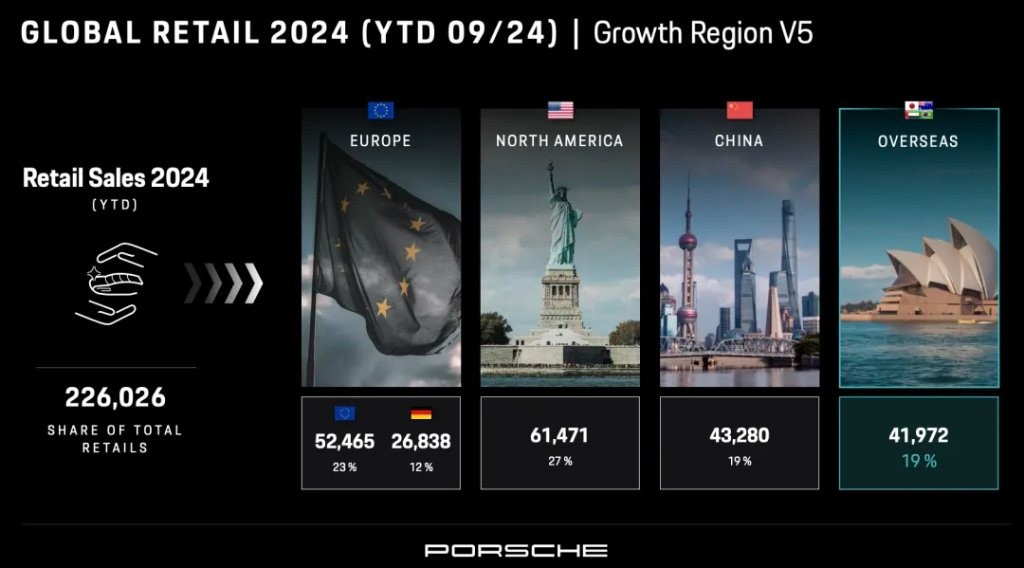
According to the latest data, as of the first three quarters of 2024, Porsche's sales in China decreased by 29% year-on-year, falling to 43,000 units, making China the only market globally where Porsche's sales decline exceeded double digits.
In light of this trend, one can't help but ask: Why has Porsche gradually lost its charm in China?
What happened to Porsche in China? Has Porsche changed, or has the Chinese market changed, with intensified market competition? Changes in consumer preferences? The impact of the macroeconomic environment? Or has Porsche's brand strategy itself been adjusted?
As the Chinese automotive market continues to develop and mature, consumers' choices for purchasing cars have become more diversified, and expectations for luxury car brands have also increased. The rise of new energy vehicles has significantly impacted traditional fuel luxury car brands.
Let us explore the deeper reasons behind Porsche's declining sales in China and analyze its issues in product, technology, and market strategy, while looking ahead to possible future paths.
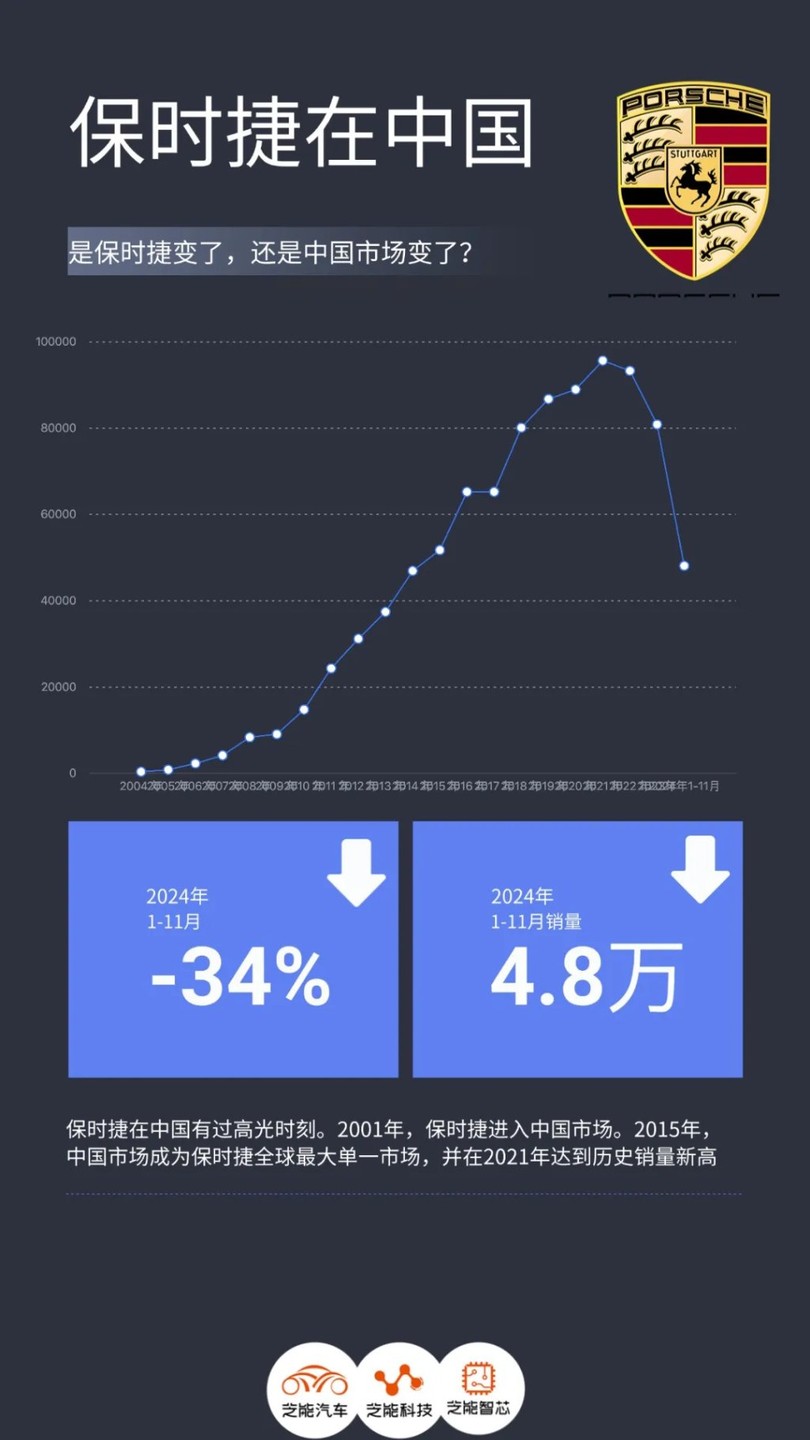
Porsche's Sales Decline in the Chinese Market
In the first 11 months of 2024, Porsche's cumulative sales in the Chinese market were only 48,000 units, a year-on-year decrease of 34%, marking the third consecutive year of negative growth. This not only falls far below the former glory of the Chinese market but also caused China to drop from being Porsche's largest single market globally to third place, behind North America and Europe.
In the third quarter of 2024, Porsche's sales in China further declined by 19% year-on-year, indicating weak signs of recovery in the Chinese market.
At the same time, imported luxury brands are facing overall pressure, but Porsche's decline is clearly higher than the market average.
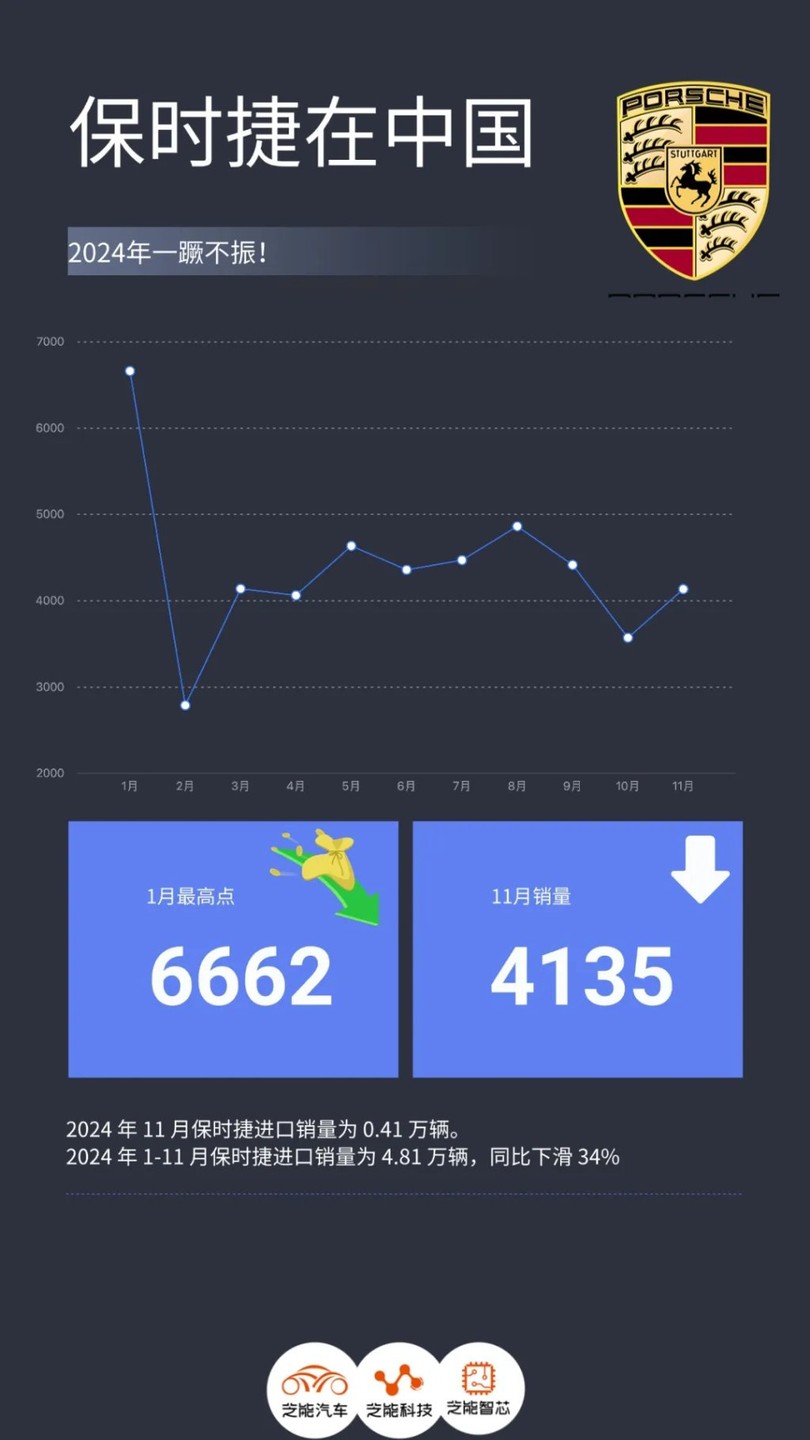
● In 2024, Porsche's sales in China showed some fluctuations.
◎ January sales were 6,662 units, starting relatively well;
◎ February sales dropped to 2,789 units, possibly affected by factors such as the Spring Festival;
◎ March sales rebounded to 4,139 units;
◎ April sales were 4,063 units, slightly down; ◎ Sales in May reached 4,636 units, showing a small peak;
◎ Sales in June were 4,359 units, slightly down;
◎ Sales in July were 4,471 units, remaining relatively stable;
◎ Sales in August were 4,863 units, rising again;
◎ Sales in September were 4,416 units, experiencing a decline;
◎ Sales in October dropped to 3,572 units;
◎ Sales in November were 4,135 units, rebounding compared to October.
The reasons behind Porsche's decline in China are due to multiple intertwined pressures, mainly including:
Changes in the market environment: As Chinese consumers show increasing interest in new energy vehicles and domestic brands rise in the luxury market, the overall market for imported luxury brands is shrinking.
We can understand this as the rapid development of the Chinese new energy vehicle market, with many domestic brands and new force car manufacturers emerging, making imported luxury cars less attractive in terms of electrification and intelligence. Aito M9, Nio, Li Auto, and even Xiaomi have significant advantages in new energy technology, intelligent configurations, and cost performance, providing low-priced alternatives.
Declining product appeal: Porsche stands out in the sports car field, but in the fiercely competitive luxury SUV and electric vehicle market, its product update speed and technological upgrades appear lagging.
Taking the Taycan as an example, its appeal in the Chinese market is no longer as strong as that of the Tesla Model S and local high-end brand new energy products. In fact, for such an expensive car, the impressive feature is surprisingly Apple CarPlay, which makes Porsche owners feel a bit embarrassed.
It's already 2025, yet this battery platform still reflects design ideas from China in 2021-2022, which is indeed a problem caused by a long development cycle.

Objectively speaking, Porsche's advantages in power have been surpassed or even completely outperformed by Chinese car manufacturers, which is a bit awkward.

We will provide a detailed comparative analysis of Porsche's platform later, examining why Porsche invested so much money so early, yet continues to lag behind in terms of parameters Dealer Conflicts: In May 2024, some Porsche dealers in China demanded subsidies by "stopping vehicle deliveries," highlighting the immense sales pressure they face.
Excessive inventory pressure has forced dealers to lower prices for promotions, severely impacting brand value and profitability. The terminal prices of models such as Taycan and Panamera are significantly lower than the official guide prices, further weakening consumer trust in the brand.
Root of the Problem: Misalignment of Products, Technology, and Market Strategy
Porsche faces multiple challenges in the Chinese market, with its core issue being the inability of product and technology innovation speed to match the rapidly changing market demands.
Porsche has launched the Taycan and planned to expand its electric vehicle lineup, but in terms of range, charging networks, and intelligent experiences, Porsche's technological and price competitiveness appears insufficient compared to the rapid development of local Chinese brands.
Porsche's product line is mainly focused on traditional SUVs like Macan and Cayenne. Faced with strong competitors like BMW and Mercedes-Benz, the advantages of these models are gradually diminishing, and the demand for high-end sports cars like the 911 has also weakened due to slowed consumption upgrades.

The dealer system is also under pressure. The frequent occurrence of inventory pressure has forced some dealers to clear stock through price reductions, which, while boosting sales in the short term, harms brand image and customer loyalty in the long run.
Porsche plans to reduce its number of dealers by about one-third in the next two years, from 154 to approximately 100, which may further weaken its market coverage in third- and fourth-tier cities.
In terms of market strategy, Porsche's understanding of localization is insufficient, especially in the localization process of R&D and production, where the localization plan has not been implemented, limiting cost optimization and affecting market competitiveness.
In facing the younger consumer group, Porsche's marketing activities lack sufficient appeal, and it has not fully leveraged its potential advantages as a high-end brand in digital experiences and services, appearing less innovative compared to emerging brands like Nio and XPeng.
To revitalize its performance in the Chinese market, Porsche needs to accelerate its electrification transformation, enrich its product structure, strengthen local operations, and enhance marketing innovation capabilities.
Looking ahead, Porsche China is actively adjusting its strategy to address market challenges, with technological advancement and improved localization capabilities seen as key driving forces.
To reverse the current situation, Porsche has taken several measures, including optimizing its organizational structure, restructuring its dealer network, and strengthening local R&D, but the effectiveness of these measures remains to be seen over time.
Accelerating electrification transformation is one of the core strategies for Porsche China. To enhance the market competitiveness of its electric vehicle products, Porsche needs to achieve breakthroughs in key technological areas such as range, intelligent driving assistance systems, and charging efficiency. Launching more cost-effective electric vehicle models that meet the expectations of Chinese consumers can not only satisfy market demand but also help the brand regain consumer favor, thereby salvaging market share Strengthening localization capabilities is crucial for Porsche's long-term development in the Chinese market. As competitors like BMW and Mercedes-Benz accelerate their local production and R&D, Porsche must speed up its efforts to cater to the specific needs of Chinese consumers by introducing more customized products and services. This not only enhances the brand's market adaptability but also effectively reduces costs, further improving the price competitiveness of its products.
Optimizing brand image and service experience is equally important. In the face of a younger consumer demographic, Porsche needs to redefine its high-end brand image, using innovative marketing strategies and unique customer service experiences to attract new customers and maintain the loyalty of existing ones. Digital interaction and service upgrades will be indispensable parts of this process, allowing the brand to remain vibrant and appealing in a rapidly changing market environment.
By focusing on technological innovation, deepening the localization process, and committing to providing an exceptional brand experience, Porsche is expected to revive its presence in the Chinese market and continue to lead trends in the luxury car sector. If it aims for volume, the key to success lies in the ability to swiftly and effectively execute the aforementioned strategies and adapt flexibly to the ever-changing market environment.
Of course, there is also the approach of making oneself smaller, which is to cater to niche markets in China!

Objectively speaking, Porsche is also exploring strategic markets; in fact, it doesn't matter for Porsche without the Chinese market, as it is just 50,000 cars!
Summary
The era of high growth in the Chinese market has ended. For Porsche, this is not only a short-term crisis but also an opportunity for strategic adjustment.
In a market environment with sudden changes in demand, Porsche must break free from its obsession with sales growth and refocus on brand value and technological innovation. The dual drive of localization and electrification may be an important path for revitalizing its presence in the Chinese market.
Article author: Tao Yanyan, source: ZhiNeng Automobile, Original Title: "Down 34%, What Happened to Porsche in China?"
Risk Warning and Disclaimer
The market has risks, and investment requires caution. This article does not constitute personal investment advice and does not take into account the specific investment goals, financial situation, or needs of individual users. Users should consider whether any opinions, views, or conclusions in this article are suitable for their specific circumstances. Investment based on this is at one's own risk

