
With a hundred billion dollars in hand, how to interpret the highlights of the listing of "the first stock of self-immunity" QYUNS-B?

荃信生物-B 上市成為 “自免第一股”,市場對其抱有高成長預期。醫藥行業正處於回撤和調整通道中,但多重利好因素帶來複蘇跡象,醫藥投資機會逐步顯現。預計美聯儲今年有望進入降息週期,醫藥行業有望迎來反彈時機。荃信生物是一家生物科技公司,擁有高成長性品種,具備稀缺與成長雙屬性,吸引了眾多投資者關注。自免領域是全球第二大治療領域,市場規模持續增長,預計到 2030 年將達 1760 億美元。荃信生物在自免賽道上具備豐富的管線佈局,有望獲得顯著上行動力。
回顧 2023 年,美聯儲持續加息、宏觀經濟復甦不確定性仍存,使得醫藥投融資市場持續低迷,而醫藥反腐等監管措施也帶來了情緒面上擾動,全年醫藥板塊仍然整體處於回撤和調整通道中。
值此市場磨底階段,隨着多重利好因素帶來複蘇跡象,醫藥板塊投資機會也正逐步顯現。
從市場層面來看,多數機構預計美聯儲今年有望進入降息週期,市場流動性預期恢復;從行業層面來看,最近召開的國家 “兩會” 釋放對醫藥行業創新發展積極扶持的信號,醫保國談政策趨於穩定,醫藥行業有望迎來反彈時機。
在篩選醫藥行業投資標的時,產品管線的稀缺性、未來市場空間、商業化變現進展等都是重要的考量因素。對於有着高成長性品種的生物科技公司,隨着臨牀數據發佈、獲批上市、產品放量等時間節點到來,股價都將在利好催化下獲得顯著上行動力。
據瞭解,荃信生物-B(02509) 自 3 月 12 日起開始在港交所公開招股,上市後將成為 “國內自身免疫第一股”。身處極具潛力的自免賽道、重磅品種商業化落地在即,其兼具稀缺與成長雙屬性已吸引了眾多投資者關注。
深耕千億自免賽道,豐富管線佈局稀缺屬性凸顯
與資本扎堆、藥企瘋狂內卷的腫瘤賽道相比,自身免疫治療領域不僅具備龐大的患者基數、快速增長的市場需求,且仍舊是一片正處於蓬勃發展期的藍海。
弗若斯特沙利文數據顯示,2022 年全球自身免疫疾病藥物市場規模約 1317 億美元,自免領域已然成為全球僅次於腫瘤的第二大治療領域;預計到 2030 年將增至 1760 億美元,其中中國市場受益於創新療法的進步及潛在醫療需求,料將錄得更高增速。

反映在資本市場層面上,自免領域熱度亦正在逐年攀升。摩根大通《2023 年度生物製藥許可和風險投資》顯示,自免領域在去年早期投資方面排名第四。
據智通財經 APP 瞭解,自身免疫疾病是指機體對自身抗原發生免疫反應而導致自身組織損害的疾病,也包括自身免疫系統超敏反應所導致的過敏性疾病,常見包括銀屑病、強直性脊柱炎、特應性皮炎、慢性鼻竇炎、哮喘和食物過敏等。作為慢性疾病,自免疾病具有難以根治、發病機制複雜等特點,長期以來患者的認知程度不高,診斷和治療率偏低。
與全球範圍內相比,國內自免領域則起步較晚。從市場角度來看,自免藥物可及性低,進口藥物長期佔主導,高昂的價格限制了患者需求;從企業角度來看,雖然國內已有數十家企業入局自免賽道,但專注於深耕自免領域的創新藥企仍然稀缺。
值得一提的是,即將於港股上市的荃信生物是國內極少數單一專注自免賽道的創新藥企,其在自免及過敏領域管線佈局、開發進度上都屬於國內第一梯隊。
據荃信生物招股書,其已披露了 9 個自免領域產品,且 IND(新藥臨牀試驗) 許可數量達到 19 個,為國內自免領域 IND 數量最多的企業之一;
從靶點佈局來看,荃信生物是國內唯一一家在白介素靶點上進行全覆蓋的 Biotech,產品涵蓋 IL-4R、IL-17、IL-23、IL-33、IL-31R 等,多方位協同佈局將有助於對自免病患進行全生命週期管理。
此外,公司有望最先商業化落地的 QX001S,是首個在中國提交 BLA 的國產烏司奴單抗生物類似藥,有望打破烏司奴單抗原研品種在國內市場一家獨大的銷售格局。
烏司奴單抗原研藥於 2009 年獲得 FDA 批准,2017 年國內獲批,是針對性抑制 IL-23 及 IL-12 通路的首款生物藥,也是全球治療銀屑病的主要療法之一。
作為銀屑病治療的第二代生物藥,IL 抑制劑的賽道並不擁擠,向來由跨國藥企佔據大多數市場份額。在 IL-17 及 IL-23 兩個常見銀屑病治療靶點中,烏司奴單抗所靶向的 IL-23 在銀屑病發病機制中處於 Th17 信號通路的上游,靶向 IL-23(包括 IL-12/23) 可實現更深和更持久的炎症緩解,在臨牀研究中顯示出更優越的長期療效及安全性。
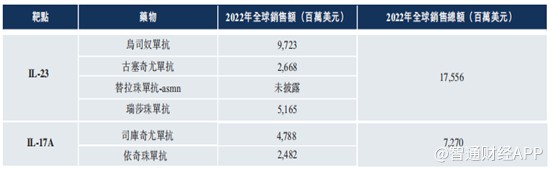
2023 年強生僅在烏司奴單抗這一項產品上就收入 108 億美元,如今這一重磅品種即將迎來國內首仿,QX001S 未來成長潛力自不待言。
荃信生物具有豐富的產品管線儲備,整體研發進展領先,隨着後續產品逐步落地,有望形成新的業績增量。包括 QX001S、QX002N 及 QX005N 在內,公司已有 6 種候選生物藥物處於不同臨牀階段。近半年內,荃信生物在研產品取得一項 BLA 受理、一項 III 期啓動、兩項 II 期達到主要臨牀終點、一項 BTD 認定、多項 IND 許可等里程碑進展。
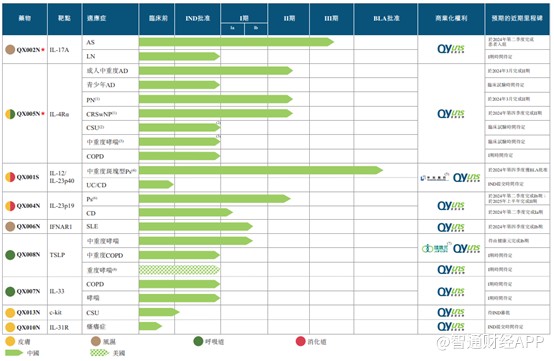
縱觀國內自免領域競爭格局,隨着國產自免創新藥走入公眾視野,往年進口藥物佔主導的局面正在被打破,國產替代的價格優勢也有助於推動滲透率進一步提升。龐大的患者基數、長期甚至終生用藥的需求,疊加經濟水平提高帶來的患者支付意願增強,都將使得自免市場的潛力被逐步發掘。
商業化捷報頻傳 核心品種將迎收穫期
除卻研發管線佈局潛力十足,荃信生物在商業化進程上也是利好頻傳。
據智通財經 APP 瞭解,烏司奴單抗生物類似藥 QX001S 已於 2023 年 8 月獲得 NMPA 受理,有望在國內率先獲批上市,將成為公司首款商業化落地的藥物;
核心產品 QX002N 是一種靶向 IL-17A 的高親和力單抗,已於 2023 年 9 月啓動針對強直性脊柱炎的 III 期臨牀試驗,預計在 2025 年下半年完成;
另一個核心產品 QX005N 旨在抑制 IL-4Rα,該靶點是一種經充分驗證可應用於廣泛適應症的靶點,公司已獲得七種適應症的 IND 批准,乃中國 IL-4Rα靶向候選藥物中適應症最多的藥物。目前 QX005N 針對 AD(特應性皮炎) 和 PN(結節性癢疹) 的 III 臨牀溝通申請已經遞交,用於治療 CRSwNP(慢性鼻竇炎伴鼻息肉) 的 II 期臨牀試驗亦已於 2023 年 4 月開始。
在商業化方面,公司已於江蘇泰州建設生產基地,年生產能力約為 300 kg 治療性抗體,還與在慢性疾病管理方面擁有豐富經驗及在自身免疫及過敏藥物方面擁有強大銷售網絡的華東醫藥達成戰略合作關係。
據瞭解,華東醫藥覆蓋中國超過 3000 家 (或 90% 以上) 三甲醫院和超過 15500 家二級及以下醫院。藉助華東醫藥的成熟銷售渠道,荃信生物的新品種商業化後有望深入基層醫療網絡,快速獲得市場份額並建立領先優勢。
荃信生物已就 QX001S 項目與華東醫藥達成商業化協議,獲得的首付款及里程碑付款合計為 5000 萬元,且未來將通過分成的形式取得該產品國內税前利潤的一半。考慮到該項藥物後續將為公司帶來源源不斷的收入,荃信生物盈利前景值得期待。
此外,荃信生物還於 2024 年 1 月與呼吸領域頭部企業健康元達成產品合作,授權健康元 QX008N(TSLP 抗體) 的中國 (包括港、澳) 的開發、生產及商業化權益,在呼吸領域增加了強有力的合作伙伴。健康元是國內呼吸領域的主要競爭者之一,2022 年全年呼吸領域銷售額 11.7 億元,2023 年前三季度呼吸領域銷售額達 11.1 億元,其呼吸製劑覆蓋國內二級以上醫院 3800 多家。
結語
近年,港交所已經出台多項改革和新政策以提升吸引力,而自 2023 年 12 月起赴港 IPO 的公司數量也呈現上升趨勢,初露回暖苗頭。
在醫藥具備 “剛需” 屬性、且人口結構老年化的情形下,醫藥行業仍是 “長坡厚雪” 的朝陽賽道,有望開啓新一輪復甦週期。低估值藴含投資機遇的當下,廣闊的市場藍海、豐富的研發管線儲備與極具潛力的新藥品種,將共同夯實荃信生物踏上高增長之路的底氣。

