
OpenAI scientists shocked TED conference: Let AI models think for 20 seconds, boosting performance by 100,000 times!

OpenAI 科學家 Noam Brown 在 TED 大會上提出,AI 模型思考 20 秒可提升性能,相當於擴大 100,000 倍並訓練 100,000 倍。他強調 “系統二思維” 是關鍵,通過自我對弈等強化學習提升推理能力。Brown 指出,AI 的巨大提升過去 5 年主要依賴規模,但現有模型需轉變為更慢、更審慎的推理方式,以解決複雜問題。
今天凌晨,知名科技媒體 Venturebeat 消息,OpenAI 高級研究科學家、德撲 AI 之父 Noam Brown,在美國舊金山舉辦的 TED AI 大會上提出了一個震驚的理論——讓 AI 模型思考 20 秒所帶來的性能提升,相當於將模型擴大 100,000 倍並訓練 100,000 倍的時間。
最初,Brown 也被這個結果嚇到了,還寫了多篇論文來驗證其真實性。他發現“系統二思維”( System 2 thinking)才是讓 AI 模型性能大幅度提升的關鍵所在。而 OpenAI 最新發布的 o1 模型同樣引入了這個技術概念,並且獲得了非常出色的性能提升。

Brown 在演講中表示,過去 5 年 AI 能獲得巨大提升可以用一個詞來概括——規模。但如今的前沿 AI 模型仍基於 2017 年推出的 Transformer 架構,主要區別在於數據規模和計算能力。
現在是時候進行訓練、推理範式轉變了,AI 模型需要超越單純的數據預處理,進入 “系統二思維” 模式,以一種更慢、更審慎的擬人化推理形式來解決超複雜的難題。
系統二思維介紹
“系統二思維” 是一個心理學概念,描述了人類處理複雜問題時所採用的深度思考方式。這個概念最初由心理學家 Daniel Kahneman 在他的著作《思考,快與慢》中提出,用來解釋人類大腦的兩種不同的思考模式。
在 Kahneman 的理論中,系統一思維是快速、直覺、自動的,它處理日常的、熟悉的任務,比如識別熟悉的面孔或者理解簡單的句子。
這種思維方式不需要我們有意識地思考,它依賴於我們的直覺和經驗,但有時也可能導致錯誤,因為它不涉及深入的邏輯推理。
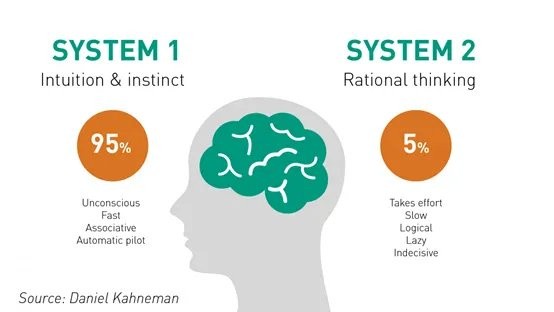
而系統二思維則是緩慢、邏輯、努力的,它涉及到深思熟慮、計算和推理。當我們面對複雜的、新穎的或者需要深入分析的問題時,就會啓動系統二思維。這種思維方式需要我們集中注意力,消耗更多的認知資源,但它可以幫助我們做出更準確和深思熟慮的決策。
Brown 直接將這個概念應用到 AI 領域,提出了一個革命性的想法:通過模擬人類的系統二思維,AI 模型可以在不增加大量數據或計算資源的情況下顯著提升性能。
以他開發的戰勝人類的德撲 AI Libratus 為例,僅讓 AI 在每手牌中思考 20 秒,就能獲得與將模型擴大 100,000 倍相同的性能提升。這種方法的核心在於讓 AI 模型在做出決策前進行更深入的分析和推理,而不是僅僅依賴於大規模數據和計算。
而 OpenAI 最新發布的 o1 模型同樣引入了系統二思維,能夠進行深度推理,模仿人類逐步解決問題的過程,通過自我對弈等強化學習訓練方式提升推理能力。
例如,在國際數學奧林匹克資格考試中,o1 模型憑藉系統二思維準確推理複雜數學公式取得 83% 的準確率,遠高於 GPT - 4o 的 13%。這對於金融、醫療、科研、編碼等對數據要求嚴謹的行業來説非常重要。
所以,系統二思維對於增強大模型的能力有很多好處,使其能夠更好地適應新的、未見過的任務和環境。在面對錯誤、不確定性和異常情況時,系統二思維還可以幫助大模型變得更加魯棒,因為它鼓勵模型採取更加謹慎和保守的策略。而在人機交互方面,模擬系統二思維能幫助大模型可以更好地理解和預測人類用户的需求和意圖,從而改善交互體驗。
AIGC 開放社區,原文標題:《OpenAI 科學家震驚 TED 大會:讓 AI 模型思考 20 秒,提升 10 萬倍性能! 》

