
The market begins to anticipate NVIDIA's next "explosive growth business": automotive chips

NVIDIA's automotive chip business has begun to attract market attention, with investors hoping it will become the next growth point. Although the data center business still accounts for the majority of revenue, its growth rate may slow down. With the rise of global autonomous driving trends, Wall Street analysts have increased their mentions of NVIDIA's automotive chips. NVIDIA's AI GPUs have played a key role in driving generative AI applications, with the data center business contributing nearly 90% of revenue in the Q3 financial report
When global data center AI chip leader NVIDIA (NVDA.US) announced its Q3 earnings for the fiscal year 2025, all investors' attention was focused on the data center business of this company, which has a market capitalization of up to $3.5 trillion. However, as NVIDIA's data center business, known as a "money-making machine," may begin to show a slowdown in growth due to a high base and excessive customer concentration, the market has started to look forward to NVIDIA's next "explosive growth business." Recently, the global craze for autonomous driving has been in full swing, and thus NVIDIA's automotive chip business, which has long seemed "very low-key," has begun to be frequently mentioned by Wall Street analysts.
Q3 financial report data shows that thanks to the explosive demand from large tech companies such as Amazon (AMZN.US), Google (GOOGL.US), Microsoft (MSFT.US), and Facebook's parent company Meta Platforms (META.US) for NVIDIA's H100/H200 and the newly launched Blackwell architecture AI GPUs, these tech companies continue to invest heavily in the construction or expansion of major AI data centers worldwide, with no signs of the fervor for artificial intelligence abating.
NVIDIA's AI GPUs are considered the core foundational hardware driving generative AI applications like ChatGPT. NVIDIA's unparalleled "explosive performance" over several consecutive quarters highlights that as major generative AI applications such as ChatGPT and Sora are successively launched, human society is gradually entering the AI era, and the demand from global enterprises and core government departments for the most essential foundational infrastructure hardware for artificial intelligence (AI)—NVIDIA's high-performance AI GPUs—continues to surge explosively.
The financial report shows that the revenue contributed by the data center business accounts for nearly 90% of NVIDIA's total revenue of $35 billion in Q3. The data center business is currently NVIDIA's most core business department, and it is the H100/H200 and Blackwell architecture AI GPUs provided by this department that offer incredibly powerful AI computing infrastructure for data centers worldwide. The financial report indicates that as the global wave of AI deployment is in full swing, this business department's revenue grew by 112% year-on-year, reaching $30.8 billion, although the growth rate has slowed compared to previous quarters. This figure significantly exceeded Wall Street's expectations and surpassed the combined revenue of Intel and AMD.
The autonomous driving wave is in full swing, and the market is extremely optimistic about NVIDIA's automotive chip business
In contrast, NVIDIA's automotive chip business department only accounts for 1% of total revenue and has long been overlooked by investors. However, compared to the declining growth rate of the data center business, its automotive chip business shows a textbook-like growth curve, with Q3's year-on-year growth expanding to 72% and a quarter-on-quarter growth of 30%, similar to the astonishing growth rate of its strongest competitor in high-performance SoC automotive chips, Qualcomm (QCOM.US).
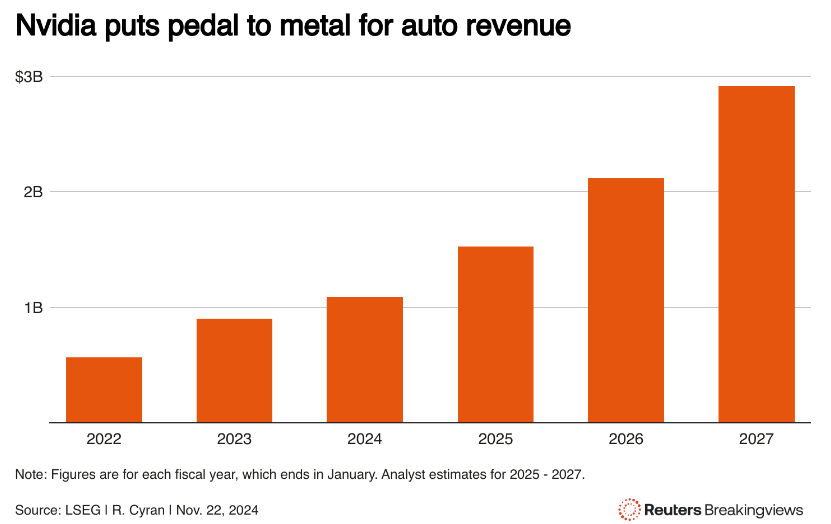
More and more Wall Street analysts indicate that as the wave of autonomous driving led by Tesla continues to sweep the globe—especially with the U.S. government's approval process for fully autonomous driving likely to accelerate significantly after Trump's administration—the demand for high-performance SoC automotive chips may experience an exponential surge. Both NVIDIA's Orin chip and the Thor chip, which will begin mass production early next year, are regarded as the "H100/H200 and Blackwell of the global automotive industry" in terms of performance and popularity.
Therefore, the automotive chip business may become a core catalyst for NVIDIA's crucial "diversification business" vision, significantly alleviating Wall Street investment institutions' cautious sentiment regarding NVIDIA's performance being overly reliant on a few American tech giants like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google.
Although cars are still primarily made of steel, the silicon elements inside vehicles, especially in the trend of "electric vehicles," are gradually becoming a significant differentiator among different automotive brands. The cool infotainment and refined navigation systems were early opportunities for chip manufacturers; now, the various intelligent features based on "vehicle networking" in electric vehicles—intelligence makes the functional indicators of electric vehicles increasingly comprehensive, with some electric vehicle models even surpassing smartphones in functionality. More importantly, the auxiliary driving and autonomous driving features that the world is competing to pursue have significantly increased the reliance on semiconductors in new complex systems.
Global electric vehicle leader Tesla (TSLA.US) and large tech companies like Waymo under Google are driving the need for more automotive chips with higher TOPS AI computing power for autonomous driving features. According to the latest forecast data from S&P Global Mobility, by 2028, the average value of chips embedded in each vehicle will rise sharply from approximately $500 in 2020 to $1,400, reflecting that "intelligence" is the major development direction in the automotive industry in recent years. Assuming 100 million vehicles are sold globally by then, this will create an unprecedented market exceeding $140 billion, with a growth rate comparable to the extremely hot AI chips for data centers.
NVIDIA's DRIVE Orin automotive chip, which fully integrates GPU, CPU, and deep learning accelerators (DLA), is regarded as the "supercomputer" for electric vehicles. Its highly integrated design allows it to handle a large number of parallel computing tasks, providing 254 TOPS of computing power. Thanks to the Ampere architecture GPU and the efficient general computing performance provided by the Arm Cortex-A78AE core, DRIVE Orin excels in high-load AI inference and high-performance computing tasks, meeting all high-performance requirements, including advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and fully autonomous driving (FSD). DRIVE Orin supports autonomous driving from level L2 to L5, capable of processing complex AI algorithms such as image recognition, object detection, and path planning, ensuring the safe operation of vehicles in complex environments NVIDIA's other more powerful DRIVE Thor is planned for mass production in 2025. According to available information, the Thor chip contains up to 77 billion transistors and provides up to 2000 TOPS (trillions of operations per second) of AI computing power. This SoC automotive chip integrates CPU, GPU, and an engine for processing Transformer large models, supporting Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) technology for efficient resource utilization and isolation.
Chip Giants Compete in Automotive Chips
In addition to Tesla choosing an independent development route to create its custom HW series SoC chips, many automotive manufacturers heavily rely on NVIDIA's system-on-chip (SoC) to support intelligent driving and infotainment systems, including autonomous driving, for their brand vehicles. This includes traditional automotive giants such as Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, Jaguar Land Rover, Volvo, and Hyundai, as well as new electric vehicle forces from China like BYD and "Wei Xiaoli."
Besides NVIDIA, other chip giants are also actively pursuing this potential market. Chip giant Qualcomm, focused on smartphone chips, has been continuously increasing its automotive chip business in recent years, achieving $899 million in automotive business revenue in the most recent quarter, a 70% year-on-year increase. While NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang can provide automotive manufacturers with graphics processing and AI technology to support infotainment systems and up to Level 5 autonomous driving, Qualcomm's exclusive background in low-power mobile chips gives it a relative advantage in wireless connectivity and general processing capabilities.
It is reported that in October, Qualcomm announced a deep collaboration with Alphabet's Google to integrate Qualcomm's automotive chips with the Android Automotive operating system. Intel (INTC.US), a long-time competitor of NVIDIA in the PC field, supports automotive chip giant Mobileye Global (MBLY.US), which is trying to leverage the advantages of camera systems into an equivalent position in the fully autonomous driving field.
These chip giants are entering a promising new automotive market and focusing on the automotive chip market, which can largely free them from a single revenue channel and gain strong support from Wall Street for the stock prices and market values of these chip companies. For example, NVIDIA will be able to reduce its reliance on a few giants: its top three customers account for more than one-third of its revenue. Meanwhile, Qualcomm can leverage new growth opportunities beyond the already mature smartphone market.
Leading electric vehicle and intelligent driving companies like Tesla may attempt to launch their proprietary internal systems, but as high-tech automotive features accelerate in popularity, other automotive manufacturers will need ready-made integrated hardware and software solutions. More importantly, from the perspective of Tesla and new Chinese automotive forces, autonomous driving capabilities are a key step for generative AI applications like ChatGPT to be applied in the real world. Any new developments in this field are likely to have beneficial impacts on humanoid robots and other potential AI terminal devices. For automotive manufacturers, creating outstanding autonomous driving systems will be the foundation for future mass production of high-end AI industrial products like humanoid robots. **
However, while these futurist opportunities have great potential, there is still a long way to go. With the significant upgrade of Tesla's FSD and the release of Robotaxi, more importantly, as the influence of Tesla CEO Elon Musk, who is "all in" on Trump, begins to span both political and business realms, fully autonomous vehicles are indeed becoming a reality, and may even accelerate in development due to the tendency for expedited reviews of Tesla's FSD and Robotaxi following Trump's return to the White House. According to informed sources, the transition team of elected President Trump plans to prioritize the federal framework for "fully autonomous vehicles" as a top review item for the U.S. Department of Transportation

