
The "rate cut dream" of the Federal Reserve is forced to be postponed. Is a major correction in the US stock market imminent?

美聯儲因最近的經濟數據可能推遲正常化計劃,甚至考慮加息,導致美股面臨更多阻力,標普 500 指數近期跌幅可能進一步加深。根據美聯儲的經濟預測摘要,他們預計 2024 年 GDP 將放緩至 1.4%,失業率將上升至 4.1%,核心 PCE 將降至 2.4%。然而,最近的數據顯示勞動力市場強勁,通脹水平也停滯在高位。根據分析師,這可能影響美聯儲的決策。
上週,標普 500 指數下跌 0.40%,這是過去十六週中的第二週下跌,也打破了連續五週的連勝紀錄。
關鍵是,自 2023 年 10 月下旬以來,標普 500 指數一直處於近乎垂直的上漲狀態。這次反彈的導火索是美聯儲的鴿派轉向——美聯儲在去年 12 月的 FOMC 會議上放棄了 “higher-for-longer” 政策,併發出了 “正常化” 政策的信號。
然而,考慮到最近的經濟數據 (更高的通脹、更強勁的增長),美聯儲似乎可能被迫推遲正常化計劃,無限期推遲,甚至考慮加息。
在這一背景下,美股似乎面臨更多阻力,標普 500 指數近期跌幅可能在未來幾周進一步加深。以下是詳細的分析。
美聯儲的 SEP 預期與數據對比
FOMC 去年 12 月的經濟預測摘要 (SEP) 顯示,美聯儲預計 2024 年:1) GDP 將放緩至 1.4%,2) 失業率將小幅上升至 4.1%,3) 核心 PCE 將降至 2.4%。
美聯儲暗示 2024 年將降息 3 次,從 5.3% 降至 4.6%,2025 年再降息 4 次,至 3.6%。這是一項正常化政策,也是軟着陸情景 (沒有衰退)。
然而,最近的數據顯示:
勞動力市場比預期強勁得多,1 月份失業率降至 3.7%,新增就業人數 35.3 萬。此外,每週初請失業金人數仍非常低,接近 20 萬人的水平,這也反映出勞動力市場緊張。
根據核心 CPI 指標,反通脹過程似乎停滯在遠高於 3% 的水平。如果以不含住房的粘性 CPI 為基準,通脹甚至可能在加速,該指標實際上在去年 11 月觸底,為 3.02%,但此後一直上升到 3.25%。一些分析師認為,1 月份核心 CPI 通脹意外上漲 0.4% 是由於住房,而住房原本預計將大幅下降。然而,從上述數據可以看到。即使消除了住房通脹,粘性通脹仍在上升。
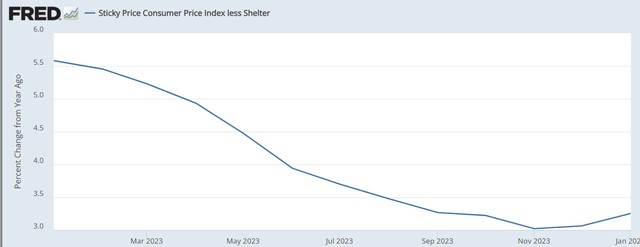
另外,儘管 1 月份零售銷售意外下降,但經濟仍遠強於預期,GDPNow 仍預測當前季度 GDP 將增長 2.9%。
因此,根據最近的經濟數據,FOMC 可能會被迫在 3 月份會議上修改 SEP,併發出 2024 年降息不到 3 次的信號,可能從調整為 0 至 2 次。
市場預期與現實
美聯儲深知經濟和金融市場穩定面臨的兩個關鍵問題:
首先,2025 年將出現一個重要的債務到期問題,許多企業將被迫為其債務進行再融資,如果利率在 2025 年之前保持高位,其中許多公司將面臨違約,這可能會導致 2025 年的信貸緊縮。商業房地產公司、地區性銀行、一般小型公司以及所有其他較弱或 “殭屍” 公司將受到最大影響。但同時,它也將對更廣泛的經濟和市場產生系統性影響。
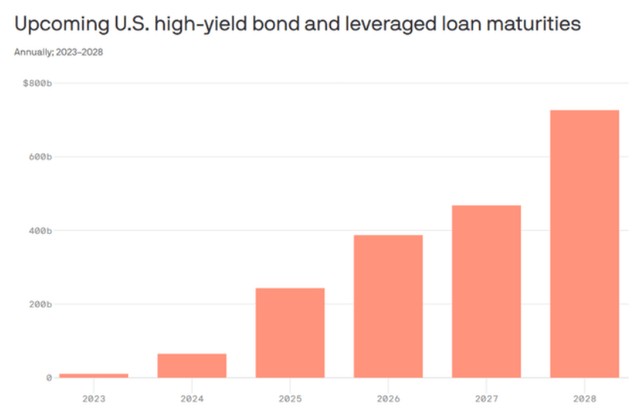
其次,先前貨幣政策緊縮的滯後效應最終將開始影響經濟,尤其是考慮到與疫情相關的儲蓄可能已經耗盡,學生貸款支付已經恢復。這可能會導致經濟衰退,而在選舉年,這種情況在政治上是不希望發生的。
因此,市場將美聯儲的鴿派轉向解讀為一個信號,即美聯儲希望避免 2024 年的經濟衰退,更重要的是避免 2025 年的債務到期問題,並在最初定價了 2024 年更激進的寬鬆政策——市場一度預期降息超過 6 次。
事實上,美聯儲確實需要在 2024 年大幅降息,以避免 2025 年的債務到期問題,所以這些都是合理的預期。然而,這種 “希望” 是通脹會崩潰,並允許美聯儲大幅削減。不幸的是,目前的數據並不支持這種 “假設”。
宏觀背景和當前市場預期
美聯儲在去年 10 月和 12 月放棄 “higher-for-longer” 政策後,金融狀況大幅放鬆。
然而,在美聯儲在 1 月份的會議上重新將立場定為 “higher-for-little-longer” 後,市場開始對美聯儲的 SEP 預測進行定價,兩年期國債走勢暗示 2024 年美聯儲將降息 3 次。
十年期國債收益率和美元都出現上升,這主要是由於實際收益率的上升——表明金融狀況正在收緊。因此,隨着兩年期國債重新定價,市場預期與美聯儲的 SEP 預測將更加一致,金融狀況將趨於收緊。
但由於人工智能熱潮,標普 500 指數卻一直在上漲,領漲的大型科技股數量不斷減少。具體來説,標普 500 指數在美聯儲 1 月份轉向鷹派立場後下跌,但該指數因 Meta(META.US) 在財報公佈後飆升 20% 而反彈。1 月份 CPI 報告公佈後,標普 500 指數出現下跌,但在英偉達 (NVDA.US)、超微電腦 (SMCI.US) 和 ARM(ARM.US) 的帶動下,該指數又一次強勁反彈。
股市面臨壓力
金融狀況可能將進一步收緊,因為兩年期國債收益率反映了美聯儲 3 次降息的定價,這也表明隨着實際收益率的上升,十年期國債收益率將上升,美元也將走強。這表明標普 500 指數將進一步下跌。
此外,美聯儲還可能修改 SEP 預測,暗示在 2024 年降息不到 3 次,這意味着金融狀況將再一步收緊,而隨着估值的收縮,股市甚至將出現更嚴重的拋售,這將對定價過高的科技股產生最大影響。
另一種可能是,1 月份零售銷售的意外下降可能會開始在其他數據中顯現出來,尤其是初請失業金人數,這可能預示着經濟衰退即將來臨,以及股市的衰退性熊市。
關於人工智能主題和大型科技 “泡沫”,英偉達將於當地時間 2 月 21 日美股盤後發佈財報,這是一個可能戳破泡沫的事件。
總結
目前,金融狀況趨於收緊,並且,隨着市場和美聯儲適應通脹現實,金融狀況可能將不得不繼續收緊。這是短期內標普 500 指數的負面催化劑。
不過,1) 美國經濟當前仍然沒有接近衰退邊緣,2) 沒有出現系統性的信貸緊縮,3) 預計美聯儲仍不會實際加息。
這説明,標普 500 指數可能只是在回調中——從技術分析上講,阻力位是之前的高點和上升通道的頂部,下一個支撐位在 4800 點左右的 50 日移動均線。

但這也並不意味着投資者不需要保持謹慎,隨着 11 月大選的臨近,以及 2025 年債務到期的臨近,除非美聯儲大幅降息,否則股市的狀況將繼續惡化。

