
Guotai Junan Securities: Can the uptrend of US mid-small cap stocks continue?

國泰君安證券發佈研報稱,美股中小盤與降息預期相關性增強,推動其上行。特朗普支持率提高也是中小盤上行的因素之一。近期羅素 2000 指數攀升超過 10.5%,資金開始向中小盤流動。美聯儲的高利率政策對科技巨頭影響不大,但對中小型企業影響明顯。中小盤股價上行的重要因素可能還包括極端頭寸的轉變。
智通財經 APP 獲悉,國泰君安證券發佈研報稱,從 2024 年 5 月以來,羅素 2000 指數與美聯儲年內降息預期表現出了較強的一致性。所以在美聯儲政策利率發生趨勢性變化階段,美股中小盤與降息預期的相關性就會逐步增強。美聯儲降息預期增強以及美國大選結果進一步清晰是推動美股中小盤上行的重要因素。此外,特朗普因電視辯論、槍擊事件支持率顯著提高,中小盤是 “特朗普交易” 的直接利好板塊。值得一提的是,極端頭寸的轉變可能也是助推中小盤股價上行的重要因素。
近期美股中小盤表現強勢,羅素 2000 指數迅速攀升,自 2024 年 7 月 9 日以來,累計增幅一度超過 10.5%。與此同時,羅素 2000 與納斯達克指數一週收益率相對波動迅速擴大,特斯拉(TSLA.US)、Alphabet(GOOG.US)第二季度財報雖然不乏亮點,但是人工智能業務盈利能力不足引發市場擔憂。避險情緒驅動下,資金開始向中小盤流動。


美股 2023 年以來持續上行的動力主要來自於 7 家大型科技公司股價的大幅上行,除此以外美股多數公司漲幅並不明顯,進入 2024 年後甚至持續貢獻反向拖累,中小盤表現也並不理想。
從 2024 年 5 月以來,羅素 2000 指數與美聯儲年內降息預期表現出了較強的一致性。美聯儲的高利率政策對科技巨頭影響並不明顯,從公司成長週期而言,他們已經度過了依靠融資進行業務擴張的階段,並且已經具備了非常優秀的 “造血” 能力,行業地位就是最好的證明。相比之下,美國中小型企業受高利率影響更為顯著,長期的高利率意味着公司高成本運營,而且公司也不具備完全將成本轉嫁消費者的能力。所以在美聯儲政策利率發生趨勢性變化階段,美股中小盤與降息預期的相關性就會逐步增強。

美聯儲降息預期增強以及美國大選結果進一步清晰是推動美股中小盤上行的重要因素。美國 6 月 CPI 數據公佈後,市場充分交易美聯儲將於 9 月降息,利率下行預期下中小盤壓力緩解。在某種程度上,美國 6 月通脹數據具有極大的里程碑意義,美國 6 月 CPI 同比增速錄得 3%,低於市場預期值 3.1%,更為重要的是,6 月 CPI 環比-0.1%,是 2020 年以來首次轉負。隨後美聯儲主席主席鮑威爾也表態,不需要等到通脹率降到 2% 才開始降息。隨着降息路徑逐步清晰,美股中小盤壓力開始緩解,羅素 2000 指數短時間內大幅上行。
此外,特朗普因電視辯論、槍擊事件支持率顯著提高,中小盤是 “特朗普交易” 的直接利好板塊。提高關税是特朗普競選的核心政策之一,大公司是高關税的直接受害者,相較之下,中小公司業務通常在美國境內居多,高關税的直接影響較小。與此同時,特朗普計劃放鬆對企業的監管,金融業是直接受益板塊,而小盤股中金融公司的佔比相對較高;寬鬆的監管環境會推動兼併和收購業務,這對小盤股而言無疑也是利好。
值得一提的是,極端頭寸的轉變可能也是助推中小盤股價上行的重要因素。CFCT(Commodity Futures Trading Commission)的數據顯示,在 6 月 CPI 數據公佈前,資產管理公司的羅素 2000 淨頭寸年內相對平穩,槓桿基金則不斷增加空頭頭寸。從 7 月開始,資管公司和槓桿基金迅速調整持倉策略,均大幅增加羅素 2000 多頭頭寸。7 月 16 日,資管公司、槓桿基金的多頭佔比分別為 59%、41%,較 7 月 2 日(55%、28%)大幅提高。
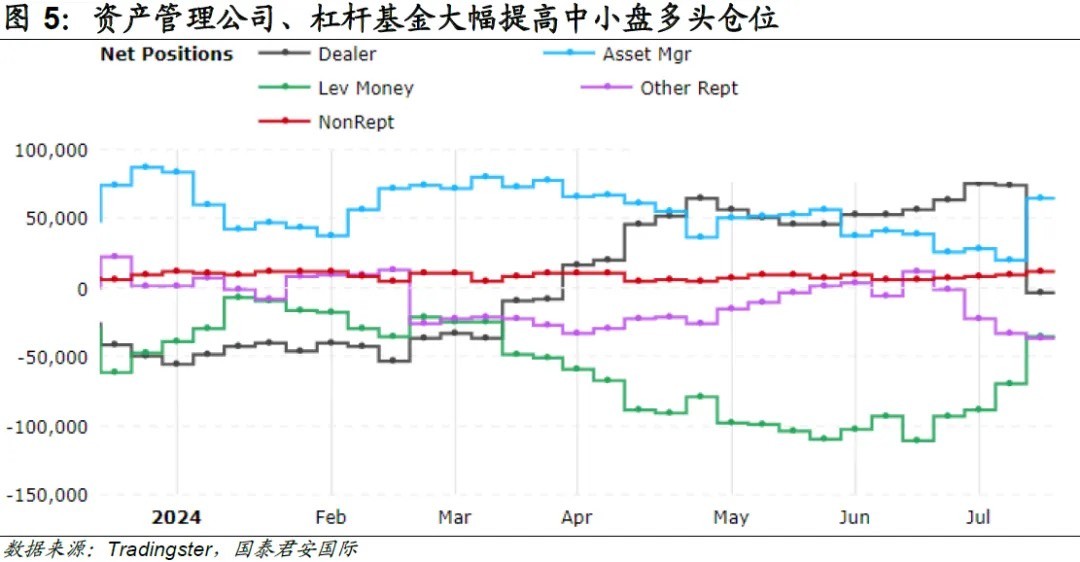
往前看,美國經濟超預期增長以及美聯儲降息在即有望持續釋放美股中小盤壓力。受消費支出以及企業對設備和庫存增長的拉動,美國第二季度實際 GDP 年化季環比錄得 2.8%,高於第一季度的 1.4%,也遠高於市場預期值 2.1%。這意味着即使通脹飆升導致美聯儲高速加息兩年後,美國經濟基礎仍然堅固。與此同時,雖然經濟增長超預期,但是美聯儲 9 月首次降息預期並未受到影響。在這種情況下,美股中小盤分子分母端壓力有望持續修復。

