
Taiwan Semiconductor's CoWoS monthly production is expected to reach 127,000 pieces next year, with NVIDIA accounting for more than half, followed closely by Broadcom and AMD

According to reports, Taiwan Semiconductor is accelerating the expansion of advanced packaging capacity, expecting to reach a monthly capacity of 127,000 CoWoS by the end of 2026, a significant increase of over 20% from the original forecast. NVIDIA accounts for more than half of the capacity, with annual bookings of 800,000 to 850,000 pieces; Broadcom ranks second, securing 240,000 pieces primarily for Meta and Google; AMD ranks third, and MediaTek has also entered the ASIC market
TSMC is accelerating the expansion of advanced packaging capacity to meet the explosive growth in demand for artificial intelligence chips.
On December 11, according to Taiwanese media reports, semiconductor equipment manufacturers revealed that TSMC, along with non-TSMC camps such as ASE Group, Amkor, and UMC, is accelerating the expansion of CoWoS capacity. By the end of 2026, TSMC's monthly capacity will reach 127,000 wafers, while the non-TSMC camp's capacity has surged from the original expectation of 26,000 wafers to 40,000 wafers, an increase of over 50%.
In terms of customer share distribution, NVIDIA continues to dominate the market, securing more than half of TSMC's CoWoS capacity, with annual bookings reaching 800,000 to 850,000 wafers. Following closely, Broadcom is expected to secure over 240,000 wafers of capacity by 2026, primarily supplying customers such as Meta and Google TPU. AMD ranks third, while MediaTek has officially entered the ASIC arena, booking nearly 20,000 wafers of capacity.
This capacity expansion plan aligns closely with Morgan Stanley's forecast from November. According to Wallstreetcn news, the firm had previously estimated that TSMC's CoWoS monthly capacity would reach 120,000 to 130,000 wafers, a significant upward revision of over 20% from the earlier estimate of 100,000 wafers. This move aims to match the newly added 3nm front-end wafer capacity to meet the enormous demand for AI chips.
It is worth noting that a previous article from Wallstreetcn stated that after NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang visited Taiwan seeking capacity for the next-generation "Rubin" platform, TSMC decided to increase the monthly 3nm front-end wafer capacity by 20,000 wafers, thereby driving a simultaneous increase in back-end advanced packaging capacity.
GPU and ASIC Demand Surge Simultaneously
The capacity expansion decisions by TSMC and non-TSMC camps stem from demand from GPU and application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) customers exceeding expectations.
Reports indicate that semiconductor equipment manufacturers have confirmed that despite the recent buzz around Google TPU and the emerging views of ASIC camps encroaching on the market, many industry players believe that NVIDIA, with its CUDA moat, remains the leader in large model training.
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang emphasized that the positioning of GPUs and ASICs is entirely different. The industry generally believes that ASICs excel in customization, low power consumption, and inference efficiency, with both developing a "symbiotic and mutually beneficial, non-exclusive" relationship.
According to order distribution, NVIDIA's share of capacity will remain unchanged at over half as capacity increases in 2027. Broadcom, which collaborates with customers such as Meta and Google TPU, has become the second-largest customer after NVIDIA.
Reports indicate that in addition to NVIDIA's AI GPU supply chain being quite complete, the growth momentum of the ASIC supply chain led by Google is highly anticipated. AWS, xAI, and other ASIC chip capacities will also gradually come online.
This sector includes major companies such as Siliconware, MediaTek, Creative, WorldChip, LianYa, WangGu, YingWei, ZhiMao, and JinXiang Electronics The major IC testing equipment manufacturer Hongjing stated that orders from ASIC customers will fully explode in the second half of 2026. MediaTek has officially entered the ASIC arena, with nearly 20,000 pieces of capacity expected in 2026, marking a further expansion of competition in this market.
In addition, according to Global Times, the United States has officially approved NVIDIA to export its advanced H200 AI GPU to China, and Intel and AMD will also be loosened, allowing the three major manufacturers to return to the Chinese AI market.
In response, the report pointed out that although the U.S. government will take a 25% cut from total sales, equipment manufacturers believe this is better than a complete ban that would result in zero profits. If the H200 can be successfully sold to China, NVIDIA's 4nm and CoWoS orders for the next year are expected to be slightly revised upward, and "the TSMC alliance will also add to the benefits."
Acceleration of Next-Generation Packaging Technology Deployment
According to Morgan Stanley analysts Tiffany Yeh and others in their research report on the 17th, after Jensen Huang's visit to Taiwan to secure capacity for its next-generation "Rubin" platform, TSMC has decided to increase its 3nm front-end wafer capacity by 20,000 pieces per month.
According to Morgan Stanley's AI tracking report, TSMC's decision to increase 20,000 pieces of 3nm front-end wafer capacity will prompt the company to simultaneously plan a significant expansion of CoWoS capacity. Analysis shows that CoWoS capacity is expected to reach at least 120,000 to 130,000 pieces per month by the end of 2026, a substantial increase from the previously expected 100,000 pieces per month.
Morgan Stanley pointed out that CoWoS, as an advanced packaging technology, is a key link supporting high-performance AI chips. As the 3nm process enters mass production, the corresponding packaging capacity must expand simultaneously to meet the delivery needs of AI customers.
It is worth noting that Morgan Stanley initially estimated TSMC's 3nm capacity in 2026 to be around 140,000 to 150,000 pieces per month, but the latest information indicates that this figure may be revised upward to 160,000 to 170,000 pieces per month.
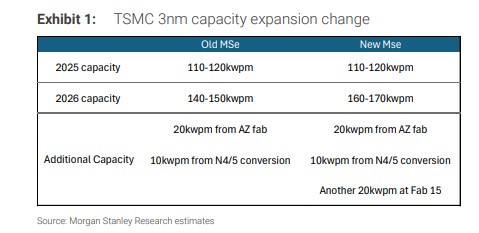
If this expansion plan is implemented, it will have a direct impact on TSMC's capital expenditures. It is estimated that the new capacity will require an additional capital expenditure of about $5 billion to $7 billion, which could raise TSMC's total capital expenditure for 2026 from the current expected $43 billion to a range of $48 billion to $50 billion.
In addition, TSMC will also refine CoWoS technology in 2027 to meet the AI demand for more logic and high-bandwidth memory (HBM), and will mass-produce CoWoS with a 9.5 times larger mask size, thereby integrating 12 or more HBM stacks into a single package using TSMC's advanced logic technology

