Turning point: In 2025, A-shares will outperform U.S. stocks!

2025 年全球股市收官,A 股在年度回報率上實現對美股的歷史性超越。以滬深 300、創業板指為代表的 A 股主要寬基指數漲幅普遍高於對標的美股指數。市場驅動邏輯呈現結構性差異:美股高度集中於 AI 算力巨頭,呈現 “頭部依賴” 特徵;而 A 股則展現出多元化格局,半導體、新材料及高端製造等板塊多點開花。
2025 年全球股市交易正式收官,全年來看,A 股在整體回報率上顯著超越了美股。
全年 A 股各大主要指數全線飄紅,滬深 300 指數全年上漲 17.66%,創業板指上漲 49.57%,上證 50 指數上漲 12.9%;與此同時,北證 50 指數上漲 38.8%,科創 50 指數上漲 35.92%。滬指 10 月 28 日一舉突破 4000 點大關,創下近十年新高。
美股方面,在經歷 4 月份的震盪後,標普 500 指數錄得 16.39% 的全年漲幅,納指險守 20.36% 的年度漲幅,道指全年上漲 12.97%。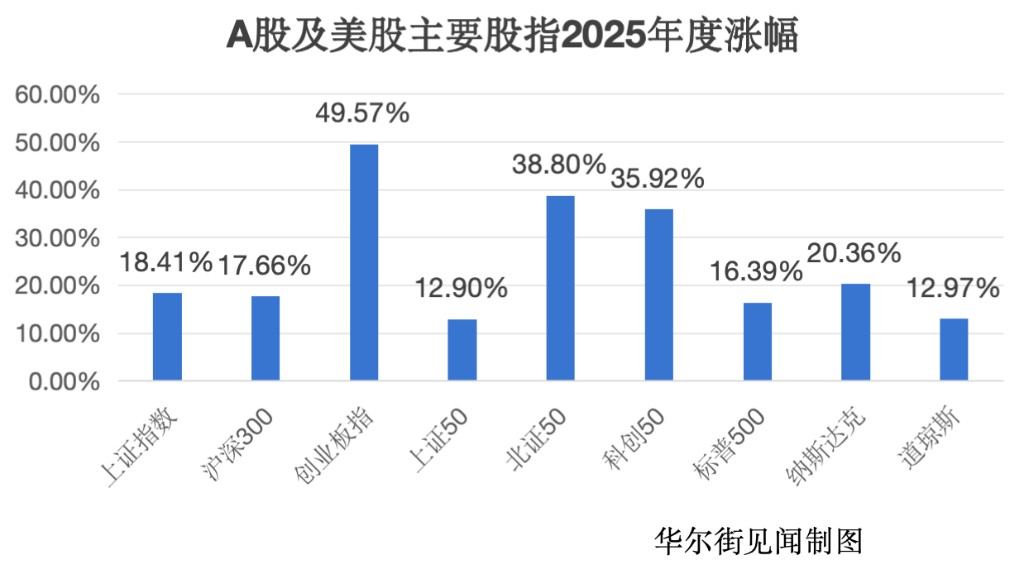
指數層面的對比顯示,A 股市場的主要寬基指數在 2025 年取得了優於美股對標指數的漲幅。其中,代表中國大盤藍籌的滬深 300 指數表現略高於美股標杆標普 500 指數;而側重科技創新與成長性的創業板指、科創 50 及北證 50 指數,其漲幅顯著超越了同樣以科技股為主的納斯達克指數。
科技敍事分化:多引擎驅動 A 股,美股高度依賴科技巨頭
在行業結構層面,兩大資本市場雖共享 “科技” 這一宏大敍事,但其實現路徑與市場生態已呈現深刻分野。
美股市場展現出鮮明的巨頭驅動格局,全年行情高度聚焦於 “AI 資本開支 - 算力產業鏈” 單一主線,以美股科技七巨頭為核心的信息技術與通信服務板塊成為市場上漲的絕對引擎,呈現出典型的頭部依賴型增長特徵。
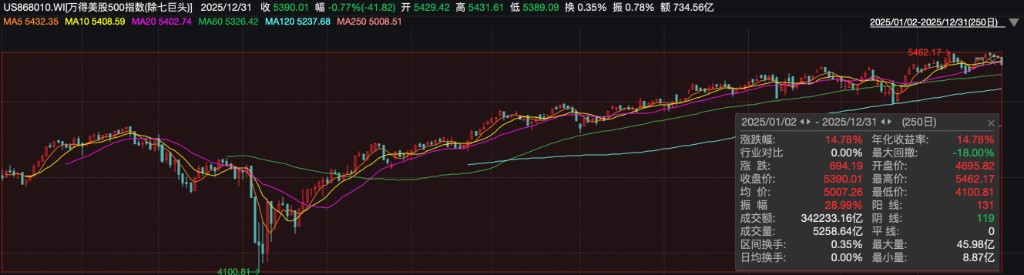
值得注意的是,這種高度集中的市場結構正積累顯著風險。當前,以 “七巨頭” 為代表的頭部企業市值已佔據標普 500 指數總市值近 40% 的歷史高位。數據顯示,2025 年剔除七大科技巨頭的萬得美股 500 指數漲幅為 14.78%,明顯落後於包含巨頭的標普 500 指數 16.39% 的整體表現。
這一差距清晰揭示了美股上漲動能的侷限性——市場廣度收窄,頭部企業與其餘成分股表現分化加劇,指數的強勢更多依賴少數巨頭的持續拉動,而非整體經濟的廣泛復甦。
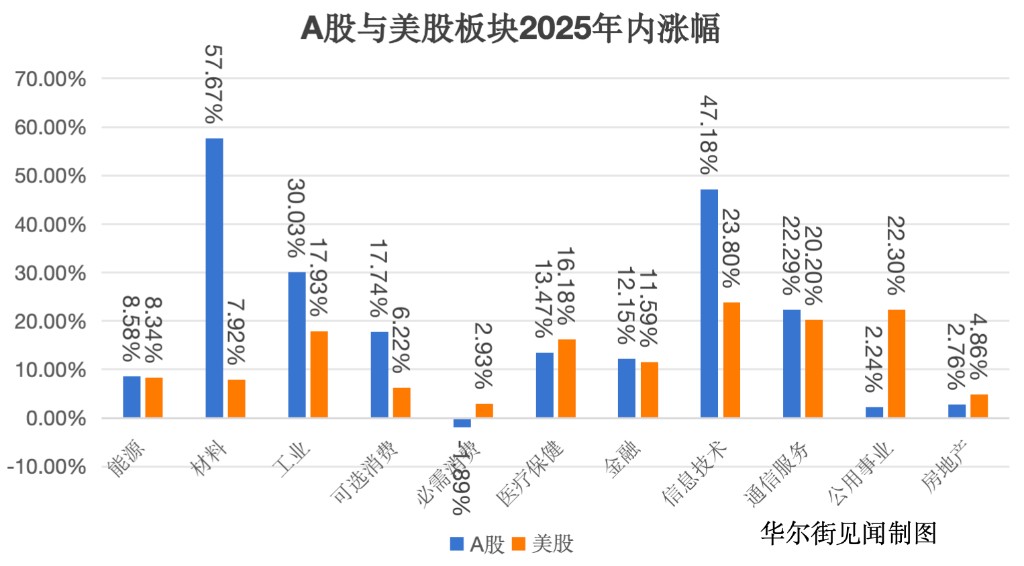
反觀 A 股市場,則展現出更為均衡與多極化的增長格局。從 2025 年行業表現數據可見,市場呈現多點開花的特徵:材料(+57.67%)、信息技術(+47.18%)、工業(+30.03%)等行業漲幅領先,共同構成了以 “先進製造產業鏈” 與 “關鍵資源供應鏈” 為核心的雙輪驅動結構。
這一結構性特徵表明,A 股行情並非由單一邏輯主導。一方面,在國產化與全球 AI 硬件需求的雙重推動下,通信、電子、計算機等科技硬件板塊持續走強;另一方面,以有色金屬為代表的戰略資源板塊表現尤為突出,這反映了在全球產業鏈重構與能源轉型背景下,資本市場對供應鏈安全與關鍵材料自主可控的戰略性重估。
“製造升級” 與 “資源保障” 的共振,實質上體現了資本市場對中國在全球產業鏈中雙重角色定位的認可:既是高端製造能力不斷提升的 “世界工廠”,也是保障關鍵原材料供應穩定的 “資源樞紐”。這種多引擎驅動的產業格局,賦予了 A 股市場更為紮實的基本面支撐和更具韌性的增長結構,與美股高度集中的科技驅動模式形成了鮮明對比。
A 股跑出兩支十倍股
據華爾街見聞,截至 12 月 31 日收盤,2025 年十大 A 股牛股分別為上緯新材、天普股份、ST 宇順、ST 亞振、勝宏科技、飛沃科技、菲林格爾、鼎泰高科、恆勃股份、順灝股份。
年內十大牛股漲幅均超過 5 倍,並湧現出兩隻十倍股。其中,上緯新材以 1689.13% 的漲幅位居榜首。

7 月起,智元機器人相關方智元恆嶽通過 “協議轉讓 + 要約收購” 的組合方式逐步收購上緯新材股權,成為公司控股股東,實控人變更為智元機器人董事長鄧泰華,這一控制權變更成為股價上漲的核心引爆點。
再加上公司的碳纖維複合材料能用到國產大飛機上,基本面也提供了堅實的支撐。
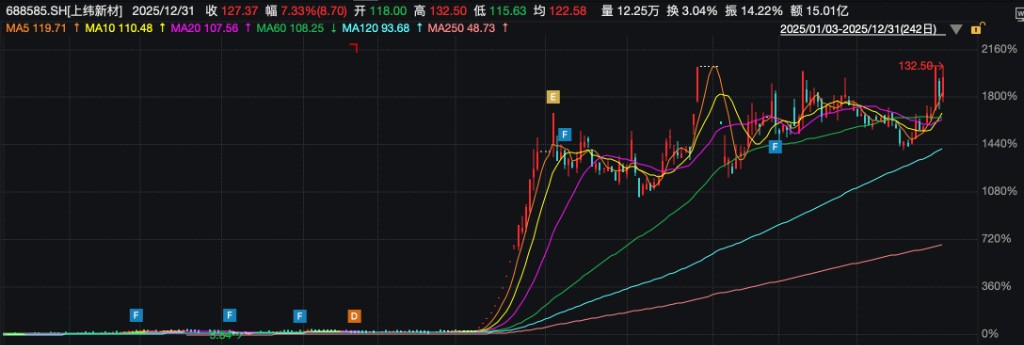
主營汽車零部件的天普股份,2025 年股價實現 16 倍暴漲,從 10 元漲到 218 元的高位,核心是 AI 芯片借殼預期與 TPU 題材的雙重發酵,引發資本合力追捧。

值得注意的是,2025 年末,國產 GPU 企業亦跑出了資本化加速度。被業界稱為 “GPU 四小龍” 的摩爾線程(688795.SH)、沐曦股份(688802.SH)、壁仞科技、燧原科技紛紛走向資本市場。
美股科技貫穿全年主線 10 大牛股存儲佔 3
美股三大指數均連續三年創新高,納指連續三年漲超 20%。
2025 年,美股市場呈現鮮明的結構性分化,由人工智能資本開支驅動的信息技術和通信服務板塊領跑市場,兩者共同構成了貫穿全年的科技主線。值得注意的是,公用事業板塊異軍突起,反映出市場在利率預期與經濟不確定性交織環境下,對穩定現金流資產的重估,以及對綠色能源轉型基礎設施投資的長期押注。
相比之下,週期性與消費板塊整體承壓。能源與材料板塊漲幅温和,可選消費與必需消費板塊明顯落後,反映出在高利率環境下,消費者支出意願和能力受到抑制。房地產板塊繼續受到高融資成本的壓制,在所有板塊中表現最為疲弱。
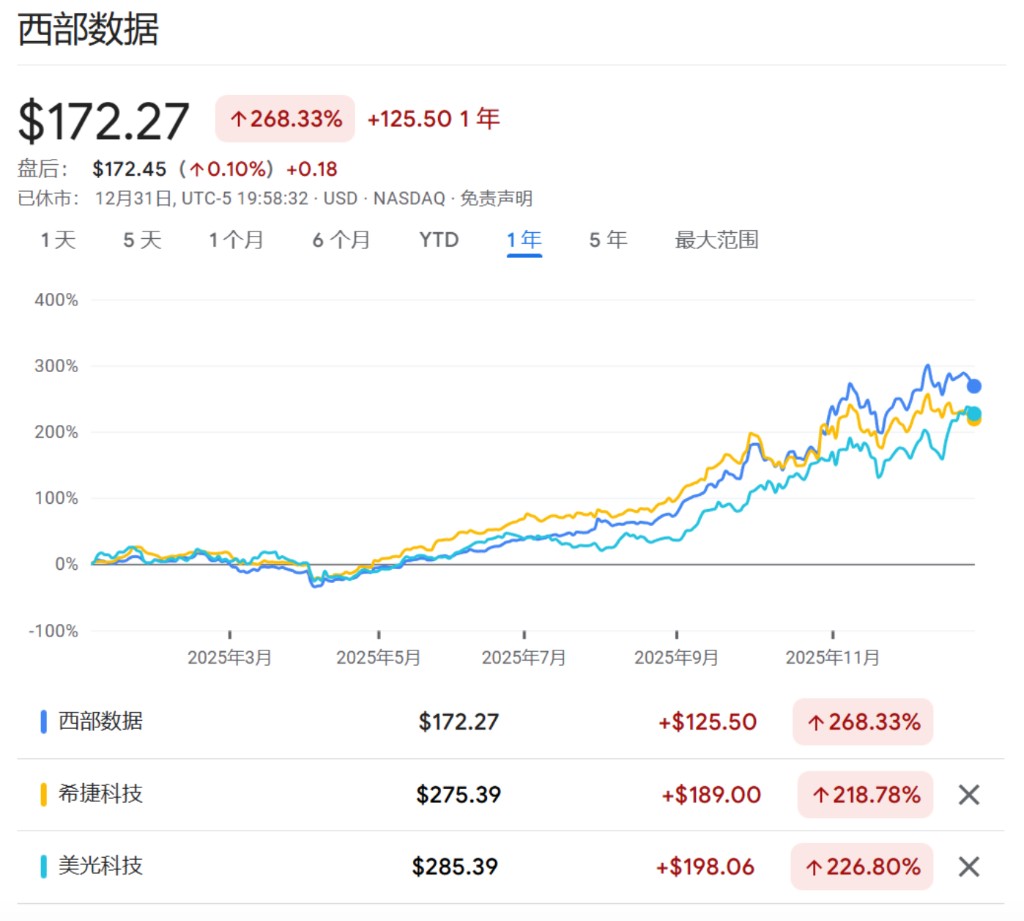
據華爾街見聞,數據存儲公司在 2025 年成為標普 500 指數最大贏家,前十大漲幅股票中有三隻來自該行業——西部數據、美光科技和希捷科技分別以 268%、227% 和 219% 的漲幅位列指數前三名。
這一表現標誌着 AI 投資主題的顯著擴散。超大規模雲服務商承諾在未來 12 個月投入超過 4400 億美元建設 AI 基礎設施,數據存儲和內存芯片公司成為這輪支出狂潮的直接受益者。微軟、亞馬遜、谷歌和 Meta 等科技巨頭的鉅額資本開支,為存儲設備製造商創造了前所未有的需求。
此外,剛剛在年底被納入標普 500 的閃迪全年漲幅高達 559%。雖然因入指時間較晚未被正式計入年度 “最佳股票”,但其從西部數據分拆後受到資本市場追捧,也再次印證了 “存儲即 AI 剛需” 的邏輯。
谷歌、英偉達領跑 Mag7
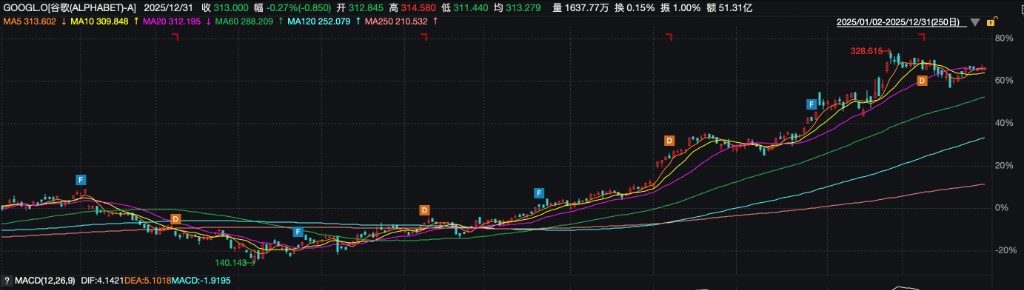
2025 年,“科技七巨頭” 走勢出現顯著分化。除谷歌(累漲約 66%)與英偉達(累漲約 39%)以顯著優勢跑贏大盤外,微軟、Meta、特斯拉等其他五家巨頭漲幅均在 11% 至 15% 之間,均未能超越標普 500 指數年度漲幅。
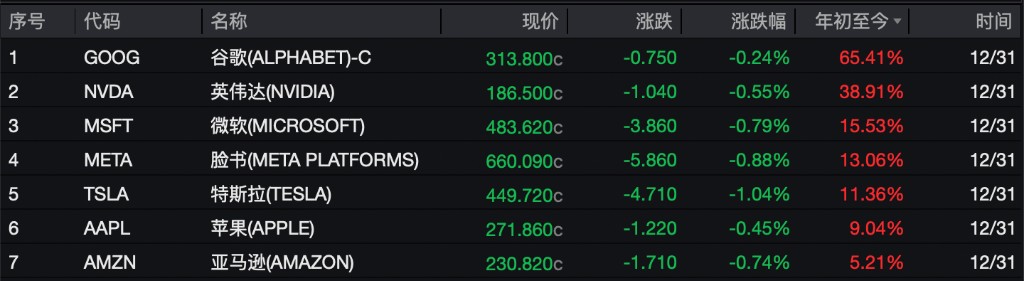
當前市場對美股科技巨頭的定價邏輯發生關鍵轉折:從為 AI“概念潛力” 定價,全面轉向為 “利潤兑現能力” 定價。這一轉變使那些能清晰展示 AI 驅動營收增長、利潤率擴張或成本優勢的公司獲得溢價,而短期業務面臨逆風或 AI 貨幣化路徑尚不明確的企業則相對承壓。這導致七巨頭走勢顯著分化。
英偉達的強勢上漲源於其在 AI 算力供應鏈中近乎壟斷的地位得到持續驗證。作為不可替代的 “軍火商”,其數據中心 GPU 在訓練與推理市場的供不應求賦予了公司強大的定價權。每個季度的業績均大幅超越市場預期,證明了爆發的需求真實且可持續,而其 CUDA 生態的深度護城河進一步強化了市場對其長期地位的信心。
谷歌的上漲動力來自於其 “TPU+Gemini+ 雲” 的垂直整合模式展現出顛覆性潛力。通過自研 TPU 在推理任務上的極致能效,公司正在對 AI 基礎設施的成本結構發起革命,這不僅提升了自身利潤率,更使其雲服務獲得了獨特的成本優勢與競爭力。